
By Tim Fisher
5G is the newest wireless networking technology that phones, smartwatches, cars, and other mobile devices, and who knows what else, will use in the coming years, but it won’t be available in every country at the same time.
North America 5G
North Americans have already seen smaller iterations of 5G networks pop up, but it’s only just now, in 2020, taking off in most areas due to the elemental challenges of 5G networks. Estimates say that by 2023, up to 32 percent of North American mobile connections will be on a 5G network.
UNITED STATES
CANADA
Canada’s Telus Mobility has given 2020 as the year 5G is available to its customers, but explains that people in the Vancouver area can expect early access.
MEXICO
In late 2017, the Mexican telecommunications company América Móvilannounced the release of 4.5 networks in anticipation of a 5G release.
PUERTO RICO
Wireless provider Claro began testing 5G in Puerto Rico in 2019.
Central America 5G
Central American countries will most likely see a slow 5G rollout.
HONDURAS
Ericsson announced in December 2018, that Tigo had chosen the company to modernize its radio access network. The deal “includes the provision of a 5G-ready multi-standard network.”
There’s no word on when 5G will reach Honduras but this agreement is an important first step.
South America 5G
South American countries with the greatest populations began to see 5G come out in spurts beginning in late 2019.
CHILE
Entel is the largest telecommunications company in Chile and has partnered with Ericsson to bring 5G wireless service to Chilean customers.
ARGENTINA
Movistar and Ericsson tested 5G systems in 2017 and will likely roll it out to customers around the same time that Chile sees 5G.
BRAZIL
After having signed an agreement to help develop and deploy the technology, we expect Brazil to usher in 5G service starting sometime in 2020.
This time range is also supported by Qualcomm director Helio Oyama, who has stated that 5G will most likely hit Brazil a few years after it’s commercially available elsewhere in 2020.
COLOMBIA
Telefónica Telecom, Colombia’s largest telecommunications company, will likely have 5G services available for customers in 2020.
PARAGUAY
Telecommunications company Tigo reached a deal with Ericsson to prepare their network for 5G. Ericsson said in December 2018, that they will “expand TIGO’s existing network and modernize the existing 2G/3G and 4G sites, making the network the best fit for TIGO to deliver 5G and IoT services in the future.”
It’s not yet clear when Tigo customers will see 5G in Paraguay, but this deal is definitely a good starting point.
ARUBA
SETAR is Aruba’s leading communications provider, and through a partnership with Nokia, the two expect full coverage on the island by 2022.
Asia 5G
5G is live in a handful of areas, with widespread coverage expected this year.
SOUTH KOREA
These three South Korean companies collaborated to bring mobile 5G to the country on December 1, 2018: SK Telecom, LG Uplus, and KT. They began with 5G service for select businesses only, but on April 5, opened up 5G for others, too, via the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G.
LG Uplus’ 5G network went live in Seoul and surrounding locations, with LS Mtron as their first customer. With over 4,000 5G base stations positioned in Incheon, Seoul, and Gyeonggi, the company planned over 7,000 more to be deployed by the end of 2018.
KT previously collaborated with Intel to showcase 5G service at the 2018 Olympic Winter Games in PyeongChang, and plans to invest over $20 billionthrough 2023 in 5G and other innovative technologies.
According to the ICT and Broadcasting Technology Policy director at the Ministry of Science and ICT, Heo Won-seok, five percent of the country’s mobile users will be on a 5G network in 2020, and 90 percent by 2026.
JAPAN
The 5G service launched with a maximum data rate of 3.4 Gbps that will increase to 4.1 Gbps in June 2020. See the NTT DOCOMO 5G smartphone pagefor device options.
In September 2018, NTT DOCOMO successfully achieved 25–27 Gbps download speeds in a 5G trial with Mitsubishi Electric. The test could be used to develop a high-speed 5G network that works with vehicles.
CHINA
Three wireless carriers launched 5G in China on October 31, 2019: China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom.
However, these companies don’t provide widespread 5G coverage just yet. The most popular areas with 5G in China right now include Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen.
SmarTone is another company looking into serving 5G in China.
QATAR
According to Ooredoo, a telecom company in Qatar that has been working on implementing 5G since 2016, they were the first company in the world to provide commercial 5G access.
5G is currently only available in Qatar, but since Ooredoo has markets in Iraq, Oman, Palestine, Maldives, Singapore, Algeria, and other countries, it isn’t a stretch to think that we’ll see 5G reach those areas in 2020.
Vodafone is another company providing 5G in Qatar. In late 2018, the company launched a 5G network in Katara Cultural Village and Souq Waqif, and before that, in Abu Hamour, Azizya, Al Mamoura, Al Rayyan, Salwa Road, and Umm Salal Mohammed. Vodafone Qatar offers unlimited 5G plans and a handful of 5G phones.
KUWAIT
Two telecommunication companies in Kuwait have launched 5G service.
On the same day, just hours later, Ooredoo announced similar news. The 5G plans available from Ooredoo include a 500 GB 45 KWD /month plan and a 1 TB 65 KWD /month plan.
STC (formerly called VIVA) is another telecom company in Kuwait that has launched 5G services. See the 5G coverage map on their website for details.
STC launched a 5G Innovation Center that was created to “explore, develop, and launch new 5G use cases in Kuwait by 2019.” As of February 2019, they had over 1,000 5G NR sites ready to go, and will roll out nationwide 5G services in partnership with Huawei.
UNITED ARAB EMIRATES
In early 2019, Etisalat UAE reached a deal with Huawei to “offer its latest state of the art network solutions including 5G wireless, 5G service oriented core and 5G ready transport network to facilitate smooth 5G technology adaption.” Etisalat UAE also selected Ericsson to deploy a 5G network in the United Arab Emirates, both mobile broadband and fixed wireless access.
5G is also coming to the United Arab Emirates from du. Officially called EITC, or Emirates Integrated Telecommunications Company, they announced in early 2019 the rollout of 700 5G sites. Their partners include Nokia and Huawei.
INDIA
According to Manoj Sinha, the minister of the Department of Telecommunications, India is set to adopt 5G this year: “When the world will roll out 5G in 2020, I believe India will be at par with them.”
On top of that, in August 2018, one of India’s largest telecom providers, Vodafone Idea Limited (previously called Idea Cellular), merged with Vodafone (which was the world’s second-largest phone company before the merger). Vodafone was already preparing for 5G, having set up “future ready technology” in 2017 by upgrading their entire radio network to support 5G.
INDONESIA
Anyone who attended the Asian Games in 2018 could have tried out 5G in Jakarta, Indonesia. A special Telkomsel SIM card was needed in order to connect to the network.
It’s unclear whether Indonesia will see commercial 5G begin to roll out in 2020 or later, but a trial of this size was a great indicator that they’re on a track of some sort. Plus, the company has partnered with Ericsson to upgrade their network in preparation for 5G.
TURKEY
In November, the company trialed 5G fixed wireless access solutions with Samsung in Istanbul. Turkcell’s CEO commented that “Today, with 5G, we have shown that the latest generation of high-speed wireless access is now possible for our customers. Our goal is clear: to make Turkey one of the first countries in the world with 5G technology.”
In early 2019, the Information and Communication Technologies Authority (BTK) in Turkey approved 5G trials in Istanbul, Izmir, and Ankara. The companies involved include Turkcell, Vodafone Turkey, and TT Mobil.
Turk Telekom is another company looking into bringing 5G to Turkey. In September 2019, the CEO said that the company is the “most ready operator for 5G in terms of fiber infrastructure prevalence.”
It’s clear that Turkcell is on the right path to providing Turkey with 5G, but it’s unclear when, exactly, customers can expect a live network.
VIETNAM
Vietnam will see 5G in 2020. According to the country’s state-owned and largest telecom company, Viettel, 5G trials were run in 2019 and they plan to have a network ready in June of 2020.
IRAN
There are a few mobile network operators in Iran, the largest of which is Mobile Telecommunication Company of Iran (MCI). MCI currently offers “4.5G” internet, which shows that they’re on a path to providing 5G in Iran. They also signed an agreement with Nokia in 2017 to develop 5G technology in Iran.
Iran’s second-largest provider, Irancell, provides both mobile and fixed wireless internet services. In late 2017, in collaboration with Ericsson, the two performed their first 5G test in Tehran and said that 5G will be available in Iran in 2020.
THAILAND
TAIWAN
Taiwan Star offers its customers a 5G upgrade experience that they can enroll in to take advantage of reduced prices once 5G rolls out in Taiwan.
SINGAPORE
StarHub announced in November 2018, that they, in partnership with Nokia, completed their first outdoor pilot of 5G on the 3.5 GHz frequency band. However, there’s no information on when StarHub will have a 5G network ready for Singaporean customers.
The IMDA (Info-communications Media Development Authority) is an organization of the Singaporean government that says a 5G network rollout will take place in 2020. There might even be two networks coming to Singapore since IMDA plans to allocate millimeter bands for 5G that “will be sufficient for at least two nationwide 5G networks.”
In fact, all four telcos might bring 5G to Singapore, including Singtel, M1, and TPG Telecom.
PHILIPPINES
The wireless communications company Smart has been testing 5G since 2016 and announced in June of 2018 the launch of 5G TehnoLab, their 5G innovation lab. Smart plans to have a 5G-ready network live for customers in 2020.
BANGLADESH
Although Bangladesh is one of the top 10 most populous countries in the world, it was very slow to roll out 4G and will likely also take much longer than other countries to implement 5G.
In early 2018, the country’s telecom regulator BTRC said that “The world will embrace 5G in 2020. So, we too will have to accept new technology and must move on to 5G. There is no option for procrastination.”
BTRC is expected to auction spectrum for 5G services before the end of 2020 to allow for widespread 5G coverage by 2026.
MALAYSIA
5G in Malaysia will likely start to be available in specific areas in 2020.
In early 2019, Maxis and Huawei and U Mobile and ZTE signed MoUs (memorandums of understanding) to collaborate on 5G deployment in Malaysia.
TM announced in late 2019 that they’d be participating in the 5G Demonstration Project to test new 5G features and learn how to best deploy 5G in Malaysia. They’ve tested using 5G for smart traffic lights, smart safety and security, and smart parking.
The Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission (MCMC) expects commercial deployment of 5G in Malaysia to take place by the third quarter of 2020.
PAKISTAN
Another tip that 5G is coming to Pakistan is that the country’s 4G pioneer Zongalso became the first company in the country to test 5G services in August 2019.
Telenor Pakistan is looking into bringing 5G to the country as well, but no dates have been released.
SAUDI ARABIA
5G has been available in Saudi Arabia through Saudi Telecom Company (STC)since June 2019, but only in specific areas of major cities and only through home routers (no mobile option, yet).
According to the company’s CEO:
5G is considered as a very important step toward digitalization and connecting everything, which supports Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 toward economic diversification.
Another 5G provider in Saudi Arabia is Zain. Over 20 locations have 5G availability, including Riyadh, Al Khobar, Dhahran, Tabuk, Hail, Sabya, Ahad Rafidah, Taif, Bisha, Najran, and Jaizan; see a 5G coverage map here. The Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G and ZTE Axon 10 Pro 5G are Zain’s 5G products.
BAHRAIN
5G in Bahrain arrived in July 2019 when STC (previously called VIVA) launched their 5G data plans. You can get mobile 5G from STC with one of their 5G phones, or 5G at home with the 5G router. The service is available in areas like Reef Island, Amwaj Islands, and Riffa Views.
KAZAKHSTAN
5G in Kazakhstan isn’t coming as soon as other countries despite the fact that it’s the ninth-largest country in the world. However, according to Prime Minister Askar Mamin, 5G is definitely in sight, calling for an “Action Plan for the implementation of 5G in Kazakhstan.”
Askar Mamin said in a meeting held in May 2019, that 5G is expected to cover all Kazakhstan settlements that have a population greater than 50 thousand people.
SRI LANKA
CAMBODIA
Service provider Smart Axiata will most likely be the first company to launch 5G in Cambodia. They were the first service provider to make 4G available in the country in 2014, and followed up in 2019 by showcasing the country’s first 5G live trial. The company expects the first few years of their 5G rollout in Cambodia to be focused on hotspots in major cities.
Africa 5G
Vodacom Group, which was the first to introduce 4G, 3G, and 2G in South Africa, is at it again with the release of a 5G trial in Lesotho in August 2018. They showcased a fixed wireless access (FWA) network using a temporary license in the 3.5 GHz band.
Rain is another South African telecom that’s rolling out 5G. From November 11, 2019 and onward, Rain customers can access the 5G network from home in parts of Johannesburg and Tshwane, with more areas becoming available throughout 2020. Check 5G coverage in South Africa with the Rain coverage map.
MTN Group Limited partnered with Ericsson in November 2018, to deploy a fixed wireless access 5G site in Midrand. Although MTN South African hasn’t announced a 5G release date, the trials and tests they’ve performed shows that they’re interested in developing 5G applications and might one day offer customers a 5G network.
NIGERIA
SENEGAL
EGYPT
MOROCCO
The two other licensed telecom companies in Morocco are Orange Morocco and Maroc Telecom, but both have been silent on a 5G deployment in the country.
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO
The release date for 5G in the Congo is unclear, but according to Léon Juste Ibombo, the country’s minister of Posts, Telecommunications and Digital Economy, we know that the 5G rollout will involve Applus and Congo Telecom:
Investments in Congo’s telecommunications sector are astronomical and the state needs credible companies to help it implement the digital economy ecosystem. This company will help our incumbent operator, Congo Telecom, to implement 5G.
TUNISIA
Ooredoo Tunisia has partnered with Nokia through the use of the company’s AirGile cloud-native core, to transition Ooredoo to a place where it can provide Tunisia customers with 5G.
KENYA
Europe 5G
5G networks are live right now in some European countries, and others will get 5G during 2020.
NORWAY
Telenor, the country’s biggest telecom operator, launched 5G in Norway in March, 2020, following early testing from 2017. These locations currently have access to the 5G network: Kongsberg, Elverum, Bodø, Askvoll, Fornebu, Kvitfjell, Longyearbyen and Spikersuppa in Oslo, and Trondheim.
Telia Company is another mobile network operator in Norway that opened its first 5G test network in December 2018. Their first trial partner was the Odeon movie theater in Oslo, marking the world’s first 5G cinema. Managing director of Telia Norway said in their December press release, “We are going to develop 5G-based solutions industry by industry, area by area.”
Telia Norway also partnered with Norwegian ISP Get to launch a 5G pilot in a family home, complete with smart tech from Futurehome. Get’s product director said “This family is far ahead of the rest of us, with a home filled with clever things connected through 5G. It is something the rest of us will not experience for several years, but it’s really fun to see what we will get with the latest technology.”
GERMANY
According to the 5G Strategy for Germany, released by Germany’s Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure (BMVI), trial installations began in 2018 with a commercial launch in 2020. 5G is planned to be rolled out “over the period to 2025.”
Deutsche Telekom rolled out 5G in Germany in Berlin, Darmstadt, Munich, Bonn, and Cologne in September 2019. Connectivity is possible through the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G, Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G, Huawei Mate 20 X 5G, and HTC 5G Hub. A total of at least 20 major German cities will have 5G by the end of 2020, and they plan to cover 90 percent of the country with 5G by 2025.
Broadband telecom provider Telefónica Germany revealed in December 2018, that in collaboration with Nokia, they finished building their “Early 5G Innovation Cluster” in Berlin. It will be used to “test and measure the performance and coverage of first 5G services in a dense urban area.”
German ISP United Internet AG is another potential 5G player, having announced in early 2019 that they’d be taking part in a 5G spectrum auction.
CZECH REPUBLIC
Vodafone will provide 5G services to customers in Karlovy Vary by July 2020. This will come a full year after the company tested a 5G holographic call in the same city.
UNITED KINGDOM
The UK’s largest network operator, EE, was the first to launch 5G in the UK on May 30, 2019. Service started in London, Cardiff, Edinburgh, Belfast, Birmingham, and Manchester, and the company now operates the 5G network in over 70 cities and towns.
EE was also the first in the world to offer the OnePlus 7 Pro 5G smartphone, but they also offer their customers the Samsung Galaxy S20 Ultra 5G, OPPO Reno 5G, LG V50 ThinQ, and other 5G phones. See their list of 5G phones for all of them.
Vodafone UK is another big mobile telecommunications provider in the UK. After testing how 5G can be used in car communications and successfully completing a holographic phone call using 5G, they launched their fifth-gen network in seven cities on July 3, bringing their total 5G coverage to 15 UK locations. The Vodafone 5G phones you can use on the network include the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G and Xiaomi Mi MIX 3 5G.
O2 has a 5G network in the United Kingdom, too. It’s currently available in 20 locations, including London, Edinburgh, Cardiff, Belfast, Leeds, Slough, Leicester, Lisburn, Manchester, Birmingham, Glasgow, Liverpool, Newcastle, Bradford, Sheffield, Bristol, and other locations. There are several 5G phonesyou can use on the O2 5G network.
CityFibre and Arqiva are two more companies with 5G trials in London. They’re in the process of creating a “5G-ready network platform nationwide that will provide the best network at the best economics for Mobile Network Operators.”
ITALY
TIM (Telecom Italia), the largest telecom provider in Italy, made 5G available in Naples, Rome, and Turin as of July 5, 2019. Their 5G network went live in another six cities before the start of 2020: Milan, Bologna, Verona, Florence, Matera, and Bari. By 2021, 120 towns and cities will be covered with TIM’s 5G network.
SWITZERLAND
The first 5G network in Switzerland went live April 17, 2019, via Swisscom. It launched in 54 towns, including Basel, Bern, Chur, Davos, Geneva, Lausanne, and Zurich. According to Swisscom, more than 90 percent of the population is covered.
The country’s second-largest telecommunications company, Sunrise, is also working to release 5G in Switzerland. They’ve already covered over 200 cities/villages with 5G, blanketing 80–98% of Dietikon, Bülach, Opfikon, Autafond, and other locations with 5G coverage. There’s a Sunrise 5G coverage map available, which also lists all the areas you can get Sunrise 5G service in Switzerland.
The company currently offers four 5G smartphones: Samsung Galaxy S10 5G, Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G, Huawei Mate 20 X 5G, and Xiaomi Mi MIX 3 5G. They also provide the HTC 5G Hub.
Salt (formerly Orange Communications) is another telecom company planning 5G in Switzerland. They revealed in January 2019 that they selected Nokia to upgrade their radio and mobile core network to provide mobile 5G services.
SPAIN
- A Coruña
- Barcelona
- Bilbao
- Gijón
- Logroño
- Madrid
- Malaga
- Pamplona
- San Sebastian
- Santander
- Seville
- Valencia
- Vigo
- Vitoria
- Zaragoza
According to Vodafone, 5G speeds at launch can be up to 1 Gbps, but will increase to up to 2 Gbps before the end of the year. You need a 5G phone from Vodafone Spain to access the network.
Orange plans to launch 5G in Spain in 2020. The company revealed in early 2019 that they made their first 5G call using their next-gen network in Valencia and will continue testing the 5G technology in Seville, Vigo, Malaga, Barcelona, Bilbao, and other cities.
AUSTRIA
Network operator A1 kicked off their path toward 5G in Austria by making their first 5G data connection in Gmünd in early January 2019. See their 5G plans and phones here.
FINLAND
DNA is another Finnish telecommunications company bringing 5G to Finland. They began offering fixed wireless access service in December, 2019. However, the company says that even with the introduction of 5G, 4G will remain the primary network technology used by most people.
RUSSIA
In 2018, Russia’s largest mobile operator, Mobile TeleSystems (MTS), partnered with Samsung to run various 5G tests that included video calls, ultra-low latency video games, and 4K video streaming.
These 5G tests were performed to show that not only is 5G coming to Russia but that Samsung’s 5G routers, tablets, and other devices are fully capable of running on a 5G network.
According to GSMA, 5G networks will cover over 80 percent of the Russian population by 2025, so it can be assumed that a big portion of the country will have access even sooner.
Another indicator that 5G in Russia is coming sooner than later is the 5G research center that’s open in Innopolis, a high-tech city in the Republic of Tatarstan.
Tele2 Russia is another telecom company bringing 5G to Russia. In collaboration with Ericsson, the company announced in February 2019 that they’d deploy 50,000 base stations in Russia. However, Tele2’s CEO says “Before launching 5G networks, Russia must first address several infrastructure issues.”, so customers might have to wait a while to receive 5G services.
LUXEMBOURG
Orange is currently the only European telecommunications company that has announced 5G plans for Luxembourg.
SLOVAKIA
It’s unclear when 5G is coming to Slovakia, but mobile operator SWAN Mobilesigned a 5G commercial contract with ZTE in early 2019 to kick off 5G rollout plans. In July 2019, the two performed the the country’s first 5G video call.
IRELAND
Vodafone is also working on fixed wireless access. In early December 2018, the company announced that they would begin trials for rural 5G broadband in Roscommon, Gorey, Dungarvan, and Clonmel, covering 20,000 premises.
Imagine is another telecom bringing 5G to Ireland. They announced the launch of their 5G-ready fixed broadband network in February 2019 and plan to build out over 300 sites to cover over one million premises by the fall of 2020.
As an Irish company, we are delighted to announce this significant investment and a new approach which will finally solve this problem and deliver much needed, fast and reliable high-speed broadband to homes, businesses and communities across regional and rural Ireland, today and into the future.
FAROE ISLANDS
CHANNEL ISLANDS
BELARUS
ROMANIA
The 5G Strategy for Romania projects an action plan with concrete tasks and deadlines for deployment, targeting the launch of services in 2020 and 5G service coverage of all urban centers and major land transport routes by 2025.
RCS & RDS is the largest Romanian cable and satellite TV company, and they also have 5G available through the Digi Mobil 5G Smart network.
HUNGARY
Vodafone is another company launching 5G in Hungary. In May of 2019, Vodafone launched Hungary’s first live 5G station in Zalaegerszeg.
CROATIA
Commercial 5G services are expected to come to Croatia by the end of 2020. Service will start in Osijek, within the region of Slavonia.
SWEDEN
Telia Company is planning a commercial launch of 5G in Sweden in 2020.
In early 2019, in collaboration with Volvo CE and Ericsson, Telia erected a 5G network in Eskilstuna with the primary focus being industrial use, such as remote-controlled machines.
A Tele2 5G network is coming to Sweden as well. They plan on providing access in 2020, but confirms that it’ll take a few years before the majority of people will have high-speed access.
POLAND
Polish mobile phone network T-Mobile Polska announced on December 7, 2018, the launch of the country’s first 5G network. It’s currently available only in the center of Warsaw via five base stations, but T-Mobile plans to develop 5G in other locations to reach the entire country.
Devices providing access to the network have been distributed to selected T‑Mobile partners, so they can be used in order to develop new business solutions and products, which will be eventually offered on the mass market.
Orange is another European mobile network operator that will launch 5G in Poland, but it won’t have a commercially available network up and running until 2020 or 2021.
Polkomtel’s Plus mobile phone network operator is rolling out 5G in Poland in 2020 with Ericsson’s 5G technology. The network will initially be deployed across Warsaw, Gdańsk, Katowice, Łódź, Poznań, Szczecin, and Wrocław.
PORTUGAL
Vodafone brought Portugal its first 5G connection on December 12, 2018, via a 5G smartphone prototype from Qualcomm. The company also tested a virtual reality game and video call on Ericsson’s 5G network.
FRANCE
French regulator Arcep expects commercial 5G rollout in France to take place in 2020.
Orange has launched 5G pilots in France in Lille, Douai, Marseille, and Châtillon.
ESTONIA
Estonia will likely see a commercially available 5G network in 2020.
According to Telia Company, the 5G network is a…
testbed for innovation and research for industry partners and academia. TalTech University´s scientists and students, as well as companies and startups can create and test solutions that require fast, high-quality data connection.
LATVIA
DENMARK
According to Telenor, the trials:
support 5G use cases such as robotics control, industrial automation, 5G/LTE dual connectivity and Fixed Wireless Access for high performance last mile connectivity.
AZERBAIJAN
ICELAND
Síminn is the leading provider of wireless communication services in Iceland. They announced in early 2019 that they’d be partnering with Ericsson to deploy 5G-ready equipment to the country.
THE NETHERLANDS
MONACO
BELGIUM
MALTA
Oceania 5G
Most major countries in Oceania saw limited 5G roll-out in 2019 with greater availability arriving in 2020.
AUSTRALIA
Australia’s second largest telecommunications company, Optus, launched 5G for mobile and home use on November 4, 2019. The launch involved over 290 5G sites in Sydney, Canberra, Adelaide, Brisbane, Melbourne, Perth, and other locations in NSW, Victoria, and Queensland. See the Optus 5G coverage mapfor details.
In November 2018, Telstra confirmed that they completed Australia’s very first 5G connection on a live network. The company’s Network Engineering Executive said that they will “continue testing over the coming months to improve data rates and overall performance in readiness for device availability.”
Vodafone has provided a 2020 release date for 5G in Australia. This is a reasonable time frame considering that not only is Vodafone the country’s largest mobile provider but because they partnered with Nokia in 2019 to agree to a 2020 5G rollout. Vodafone users can expect 5G in these areas.
NEW ZEALAND
First allocation of 5G spectrum will be the 3.5 GHz band, with national rights to this portion of the spectrum expected to be auctioned early in 2020.
Vodafone is another 5G player in New Zealand. They switched on 5G in parts of Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, and Queenstown on December 10, 2019. See Vodafone New Zealand’s 5G-ready phones.
GUAM
According to SK Telecom, the plan has been to start the 5G rollout in Guam in “highly concentrated central areas of cities, local business customers and areas that lack fixed-line infrastructure.” Coverage will then extend to wider areas.
Source: Lifewire
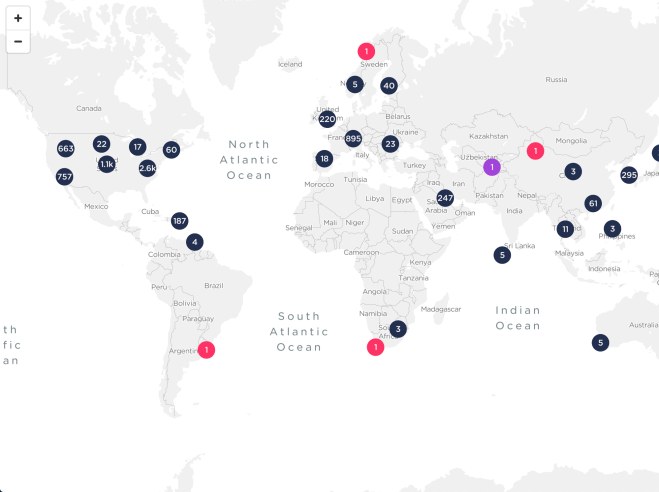 The interactive Ookla 5G Map tracks 5G rollouts in cities across the globe. Updated weekly from verified public sources and Ookla data, you can follow operators’ newest 5G networks on @Ookla5GMap. Click above graphic to go to the interactive map…
The interactive Ookla 5G Map tracks 5G rollouts in cities across the globe. Updated weekly from verified public sources and Ookla data, you can follow operators’ newest 5G networks on @Ookla5GMap. Click above graphic to go to the interactive map…


 Edward Snowden, the man who exposed the breadth of spying at the US’s National Security Agency, has warned that an uptick in surveillance amid the coronavirus crisis could lead to long-lasting effects on civil liberties.
Edward Snowden, the man who exposed the breadth of spying at the US’s National Security Agency, has warned that an uptick in surveillance amid the coronavirus crisis could lead to long-lasting effects on civil liberties. Johnny Liberty, Editor’s Note: As Edward Snowden was correct to reveal to the international press (at the sacrifice of his own well-being and freedom) that the NSA had abused their power and broke the law in gathering metadata on every American citizen, giving more power to the government is not a wise move regardless of the reason. Once they have that power, they’ll always have it (and will eventually abuse it). For example, the USA Patriot Act continues to be in force today without a tangible terrorist threat. Your civil liberties and sovereign rights continue to be compromised daily.
Johnny Liberty, Editor’s Note: As Edward Snowden was correct to reveal to the international press (at the sacrifice of his own well-being and freedom) that the NSA had abused their power and broke the law in gathering metadata on every American citizen, giving more power to the government is not a wise move regardless of the reason. Once they have that power, they’ll always have it (and will eventually abuse it). For example, the USA Patriot Act continues to be in force today without a tangible terrorist threat. Your civil liberties and sovereign rights continue to be compromised daily.
 By Julie Bossmann
By Julie Bossmann
