Source: BitChute
Former Cell Phone Company Boss Blows Whistle on 5G Coronavirus | BitChute
Source: BitChute
Source: BitChute

The Japanese government is planning to release more than one million tons of contaminated radioactive water from the Fukushima nuclear plant into the Pacific Ocean, angering fishermen, local media have reported.
Japan has debated what to do with the rapidly increasing store of radioactive wastewater for years, and now the decision to release it into the ocean could be confirmed by the end of the month.
Currently, Japan houses the water in more than 1,000 tanks, but with 170 additional tons of the radioactive by-product being produced every day, storage space is quickly running out.
It is estimated that all tanks will have reached maximum capacity by the summer of 2022 and Japanese Chief Cabinet Secretary Katsunobu Kato said on Friday that the decision was one they could “not keep delaying,” Kyodo News reported.
The water is used to cool the Fukushima nuclear reactor core, which went into meltdown after the catastrophic 2011 earthquake and tsunami that struck the plant.
The government previously considered building more tanks to house the additional water, or attempting to evaporate the water into the atmosphere, but an advisory panel recommended releasing it into the ocean as the most efficient solution. However, the release process is not expected to begin until 2022 and is likely to take 30 years to complete.
The prospect of an ocean release has reignited concerns among local fishermen who fear it could destroy their industry.
“We are terrified that if even one fish is found to have exceeded the [radiation] safety standards after the treated water is released, people’s trust in us will plummet,” Kyodo News quoted a local fisherman as saying.
Hiroshi Kishi, who heads a confederation of Japanese fishing cooperatives told officials last week that the release could have a “catastrophic impact” on the industry.
Fishing was completely halted following the 2011 disaster, and despite a recent recovery, fishermen in the region continue to face international trade restrictions. South Korea, which still bans all fish imports from the region, has described the proposal as a “grave threat.”
The initial meltdown in 2011 forced the evacuation of 150,000 people from within 20km of the plant as well as from outside areas that experienced high levels of fallout. The clean-up process is expected to take many more years to complete.
Source: RT
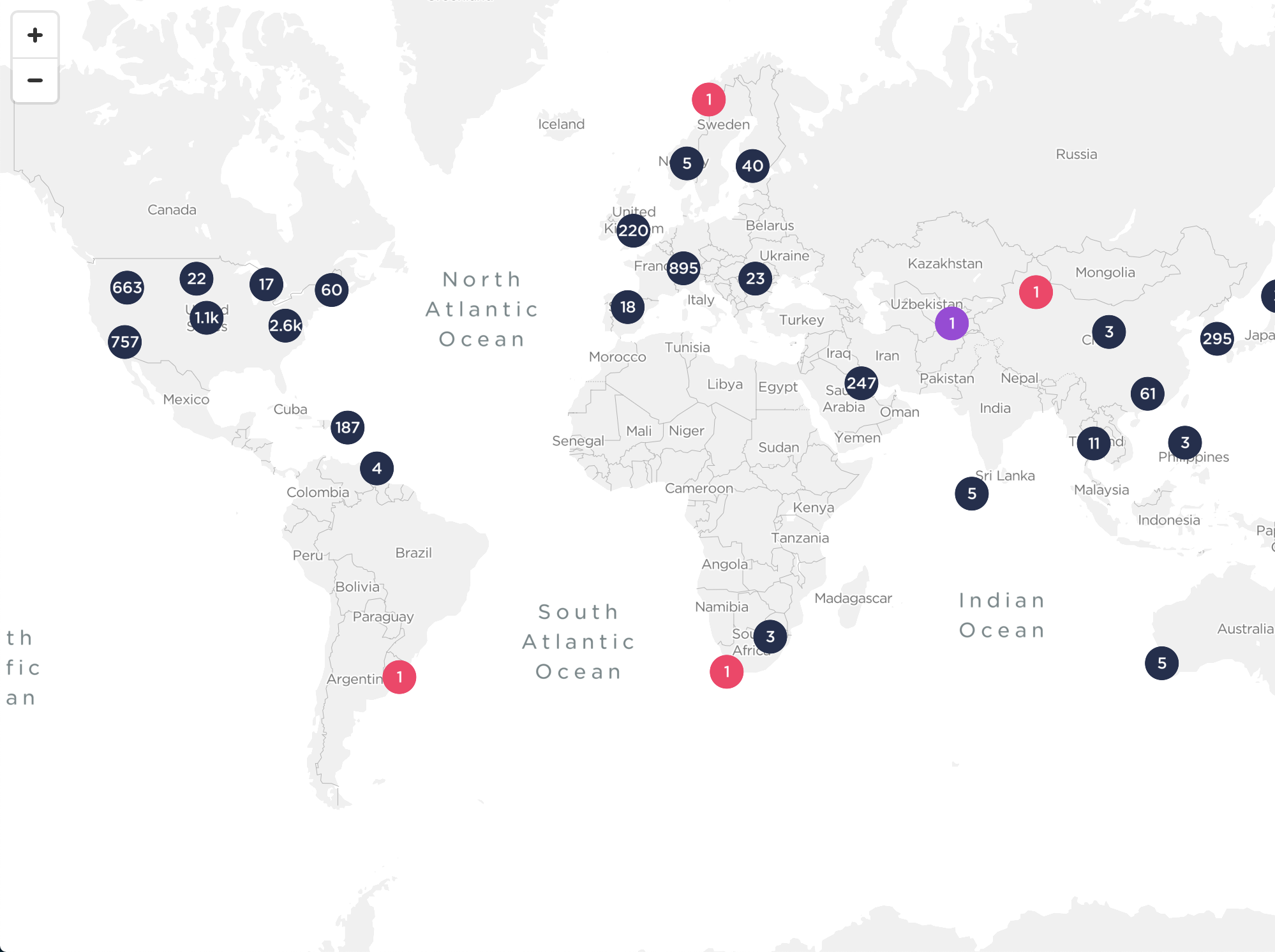 The interactive Ookla 5G Map tracks 5G rollouts in cities across the globe. Updated weekly from verified public sources and Ookla data, you can follow operators’ newest 5G networks on @Ookla5GMap. Click above graphic to go to the interactive map…
The interactive Ookla 5G Map tracks 5G rollouts in cities across the globe. Updated weekly from verified public sources and Ookla data, you can follow operators’ newest 5G networks on @Ookla5GMap. Click above graphic to go to the interactive map…
Source: Speedtest
5G is the newest wireless networking technology that phones, smartwatches, cars, and other mobile devices, and who knows what else, will use in the coming years, but it won’t be available in every country at the same time.
Some estimates forecast that by 2023, 5G will support more than 10 percent of the world’s mobile connections. For daily updates on how 5G is developing around the globe, see 5G: The Latest News & Updates. Also check out which 5G phones are available right now and when others are coming.
North Americans have already seen smaller iterations of 5G networks pop up, but it’s only just now, in 2020, taking off in most areas due to the elemental challenges of 5G networks. Estimates say that by 2023, up to 32 percent of North American mobile connections will be on a 5G network.
5G fixed wireless broadband internet from Verizon, C Spire, and Starry is currently available at a handful of locations, and Verizon, AT&T, Sprint, and T-Mobile have mobile 5G services available in various cities. More areas will get at-home and mobile 5G this year, from those companies and others like U.S. Cellular.
Rogers Communications began rolling out a 5G network in early 2020 after investing over $4 billion USD on 5G in 2019. They also made a 5G test site on campus at the University of British Columbia. Learn more about the plans Rogers has for 5G to see when they expect a live network around the country.
Canada’s Telus Mobility has given 2020 as the year 5G is available to its customers, but explains that people in the Vancouver area can expect early access.
In late 2017, the Mexican telecommunications company América Móvilannounced the release of 4.5 networks in anticipation of a 5G release.
Its CEO says 5G should be available sometime in 2020 depending on the technology that’s available at that time.
Wireless provider Claro began testing 5G in Puerto Rico in 2019.
Central American countries will most likely see a slow 5G rollout.
Ericsson announced in December 2018, that Tigo had chosen the company to modernize its radio access network. The deal “includes the provision of a 5G-ready multi-standard network.”
There’s no word on when 5G will reach Honduras but this agreement is an important first step.
South American countries with the greatest populations began to see 5G come out in spurts beginning in late 2019.
Entel is the largest telecommunications company in Chile and has partnered with Ericsson to bring 5G wireless service to Chilean customers.
Movistar and Ericsson tested 5G systems in 2017 and will likely roll it out to customers around the same time that Chile sees 5G.
After having signed an agreement to help develop and deploy the technology, we expect Brazil to usher in 5G service starting sometime in 2020.
This time range is also supported by Qualcomm director Helio Oyama, who has stated that 5G will most likely hit Brazil a few years after it’s commercially available elsewhere in 2020.
Telefónica Telecom, Colombia’s largest telecommunications company, will likely have 5G services available for customers in 2020.
In July 2018, Ericsson and Telefónica Telecom demonstrated a 5G data transfer of 27 Gbps in Bogotá.
Telecommunications company Tigo reached a deal with Ericsson to prepare their network for 5G. Ericsson said in December 2018, that they will “expand TIGO’s existing network and modernize the existing 2G/3G and 4G sites, making the network the best fit for TIGO to deliver 5G and IoT services in the future.”
It’s not yet clear when Tigo customers will see 5G in Paraguay, but this deal is definitely a good starting point.
SETAR is Aruba’s leading communications provider, and through a partnership with Nokia, the two expect full coverage on the island by 2022.
5G is live in a handful of areas, with widespread coverage expected this year.
These three South Korean companies collaborated to bring mobile 5G to the country on December 1, 2018: SK Telecom, LG Uplus, and KT. They began with 5G service for select businesses only, but on April 5, opened up 5G for others, too, via the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G.
The SK Telecom service provider started offering 5G service to a wide population on April 5 via their four 5G plans. This came after the company started a limited 5G service with the Myunghwa Industry manufacturing company. SKT’s 5G service plans come after trialing 5G in 2017 and using 5G in their self-driving test site K-City.
LG Uplus’ 5G network went live in Seoul and surrounding locations, with LS Mtron as their first customer. With over 4,000 5G base stations positioned in Incheon, Seoul, and Gyeonggi, the company planned over 7,000 more to be deployed by the end of 2018.
KT Corporation launched pre-commercial 5G services at Lotte World Tower in Seoul and six other areas including Jeju, Ulleungdo, and Dokdo. On April 5, the company launched unlimited 5G services called KT 5G Super Plans, and expanded coverage in Korea to a total of 85 cities by the end of 2019.
KT previously collaborated with Intel to showcase 5G service at the 2018 Olympic Winter Games in PyeongChang, and plans to invest over $20 billionthrough 2023 in 5G and other innovative technologies.
According to the ICT and Broadcasting Technology Policy director at the Ministry of Science and ICT, Heo Won-seok, five percent of the country’s mobile users will be on a 5G network in 2020, and 90 percent by 2026.
NTT DOCOMO is Japan’s largest wireless carrier. They’ve been studying and experimenting with 5G since 2010 and launched pre-commercial 5G services in September 2019 before officially starting 5G services on March 25, 2020.
The 5G service launched with a maximum data rate of 3.4 Gbps that will increase to 4.1 Gbps in June 2020. See the NTT DOCOMO 5G smartphone pagefor device options.
In September 2018, NTT DOCOMO successfully achieved 25–27 Gbps download speeds in a 5G trial with Mitsubishi Electric. The test could be used to develop a high-speed 5G network that works with vehicles.
KDDI and Rakuten are providing 5G services in 2020 as well. KDDI’s 5G network launched on March 26.
SoftBank began its 5G services on March 27 for 1,000 yen /month ($9 USD).
Three wireless carriers launched 5G in China on October 31, 2019: China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom.
However, these companies don’t provide widespread 5G coverage just yet. The most popular areas with 5G in China right now include Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen.
3 Hong Kong launched 5G on April 1, 2020. According to the press release, 5G is expected to cover indoor and outdoor areas in all districts in Hong Kong within 2020.
SmarTone is another company looking into serving 5G in China.
According to Ooredoo, a telecom company in Qatar that has been working on implementing 5G since 2016, they were the first company in the world to provide commercial 5G access.
5G is currently only available in Qatar, but since Ooredoo has markets in Iraq, Oman, Palestine, Maldives, Singapore, Algeria, and other countries, it isn’t a stretch to think that we’ll see 5G reach those areas in 2020.
Ooredoo, in partnership with Ericsson, will also use 5G for home broadband service.
Vodafone is another company providing 5G in Qatar. In late 2018, the company launched a 5G network in Katara Cultural Village and Souq Waqif, and before that, in Abu Hamour, Azizya, Al Mamoura, Al Rayyan, Salwa Road, and Umm Salal Mohammed. Vodafone Qatar offers unlimited 5G plans and a handful of 5G phones.
Two telecommunication companies in Kuwait have launched 5G service.
Zain was the first, announcing the 5G launch in June 2018. You can sign up herefor a 500 GB, 1 TB, 2 TB, or 4 TB plan. Currently, the only device you can use on Zain’s 5G network in Kuwait is the 5G Bolt router, for home broadband internet.
On the same day, just hours later, Ooredoo announced similar news. The 5G plans available from Ooredoo include a 500 GB 45 KWD /month plan and a 1 TB 65 KWD /month plan.
STC (formerly called VIVA) is another telecom company in Kuwait that has launched 5G services. See the 5G coverage map on their website for details.
STC launched a 5G Innovation Center that was created to “explore, develop, and launch new 5G use cases in Kuwait by 2019.” As of February 2019, they had over 1,000 5G NR sites ready to go, and will roll out nationwide 5G services in partnership with Huawei.
UAE 5G became available via Etisalat UAE on May 30, 2019. There are several 5G phones available for purchase.
In early 2019, Etisalat UAE reached a deal with Huawei to “offer its latest state of the art network solutions including 5G wireless, 5G service oriented core and 5G ready transport network to facilitate smooth 5G technology adaption.” Etisalat UAE also selected Ericsson to deploy a 5G network in the United Arab Emirates, both mobile broadband and fixed wireless access.
5G is also coming to the United Arab Emirates from du. Officially called EITC, or Emirates Integrated Telecommunications Company, they announced in early 2019 the rollout of 700 5G sites. Their partners include Nokia and Huawei.
Virgin Mobile is another 5G-ready company deploying this next-gen network across the UAE. See which 5G phones Virgin Mobile has available.
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India released this PDF in late 2017 that outlines the 5G standard draft and shows a timeframe for when 5G should be deployed around the world.
According to Manoj Sinha, the minister of the Department of Telecommunications, India is set to adopt 5G this year: “When the world will roll out 5G in 2020, I believe India will be at par with them.”
On top of that, in August 2018, one of India’s largest telecom providers, Vodafone Idea Limited (previously called Idea Cellular), merged with Vodafone (which was the world’s second-largest phone company before the merger). Vodafone was already preparing for 5G, having set up “future ready technology” in 2017 by upgrading their entire radio network to support 5G.
Reliance Jio is another mobile network operator in India that plans to provide 5G services in 2020, as well as their own 5G handsets.
Another Indian telecom company working on 5G is Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL). They signed a memorandum of understanding with Ciena, a networking systems company, in early 2019 to prepare its network for 5G.
A 5G test network is being erected in 2020 from Cavil Wireless.
Anyone who attended the Asian Games in 2018 could have tried out 5G in Jakarta, Indonesia. A special Telkomsel SIM card was needed in order to connect to the network.
It’s unclear whether Indonesia will see commercial 5G begin to roll out in 2020 or later, but a trial of this size was a great indicator that they’re on a track of some sort. Plus, the company has partnered with Ericsson to upgrade their network in preparation for 5G.
Turkcell is Turkey’s largest mobile phone operator. In early 2017, the company completed a 24.7 Gb/s 5G trial with Ericsson, and in September of 2018 announced an agreement with Nokia to develop 5G technologies.
In November, the company trialed 5G fixed wireless access solutions with Samsung in Istanbul. Turkcell’s CEO commented that “Today, with 5G, we have shown that the latest generation of high-speed wireless access is now possible for our customers. Our goal is clear: to make Turkey one of the first countries in the world with 5G technology.”
In early 2019, the Information and Communication Technologies Authority (BTK) in Turkey approved 5G trials in Istanbul, Izmir, and Ankara. The companies involved include Turkcell, Vodafone Turkey, and TT Mobil.
Turk Telekom is another company looking into bringing 5G to Turkey. In September 2019, the CEO said that the company is the “most ready operator for 5G in terms of fiber infrastructure prevalence.”
It’s clear that Turkcell is on the right path to providing Turkey with 5G, but it’s unclear when, exactly, customers can expect a live network.
Vietnam will see 5G in 2020. According to the country’s state-owned and largest telecom company, Viettel, 5G trials were run in 2019 and they plan to have a network ready in June of 2020.
Mobifone is another mobile network operator that plans to launch 5G in Vietnam by June, 2020.
There are a few mobile network operators in Iran, the largest of which is Mobile Telecommunication Company of Iran (MCI). MCI currently offers “4.5G” internet, which shows that they’re on a path to providing 5G in Iran. They also signed an agreement with Nokia in 2017 to develop 5G technology in Iran.
Iran’s second-largest provider, Irancell, provides both mobile and fixed wireless internet services. In late 2017, in collaboration with Ericsson, the two performed their first 5G test in Tehran and said that 5G will be available in Iran in 2020.
Advanced Info Service (AIS), the country’s largest mobile phone operator, will launch 5G in Thailand in 2020.
Taiwan Star offers its customers a 5G upgrade experience that they can enroll in to take advantage of reduced prices once 5G rolls out in Taiwan.
StarHub announced in November 2018, that they, in partnership with Nokia, completed their first outdoor pilot of 5G on the 3.5 GHz frequency band. However, there’s no information on when StarHub will have a 5G network ready for Singaporean customers.
The IMDA (Info-communications Media Development Authority) is an organization of the Singaporean government that says a 5G network rollout will take place in 2020. There might even be two networks coming to Singapore since IMDA plans to allocate millimeter bands for 5G that “will be sufficient for at least two nationwide 5G networks.”
In fact, all four telcos might bring 5G to Singapore, including Singtel, M1, and TPG Telecom.
The wireless communications company Smart has been testing 5G since 2016 and announced in June of 2018 the launch of 5G TehnoLab, their 5G innovation lab. Smart plans to have a 5G-ready network live for customers in 2020.
In November 2018, Smart rolled out their first 5G cell sites in the Philippines. They were set up in Makati Central Business District (Makati CBD) and at the Clark Freeport Zone in Pampanga.
In Smart’s 5G testing, they’ve managed to achieve speeds of over 14 Gb/s, and have completed a 5G-enabled video call.
Globe Telecom has a 5G fixed wireless broadband service called Globe At Home Air Fiber 5G, offering speeds up to 100 Mbps and data packages as large as 2 TB.
NOW Telecom is another company planning to deploy 5G in the Philippines.
PLDT is hoping to have a 5G network up and running before June 2020.
Although Bangladesh is one of the top 10 most populous countries in the world, it was very slow to roll out 4G and will likely also take much longer than other countries to implement 5G.
In early 2018, the country’s telecom regulator BTRC said that “The world will embrace 5G in 2020. So, we too will have to accept new technology and must move on to 5G. There is no option for procrastination.”
BTRC is expected to auction spectrum for 5G services before the end of 2020 to allow for widespread 5G coverage by 2026.
BTCL and Banglalink are two companies to watch for 5G in Bangladesh.
5G in Malaysia will likely start to be available in specific areas in 2020.
In early 2019, Maxis and Huawei and U Mobile and ZTE signed MoUs (memorandums of understanding) to collaborate on 5G deployment in Malaysia.
TM announced in late 2019 that they’d be participating in the 5G Demonstration Project to test new 5G features and learn how to best deploy 5G in Malaysia. They’ve tested using 5G for smart traffic lights, smart safety and security, and smart parking.
The Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission (MCMC) expects commercial deployment of 5G in Malaysia to take place by the third quarter of 2020.
5G might go live for consumers this year given that the Pakistan Telecommunication Authority prepared for public 5G trials in 2019.
Another tip that 5G is coming to Pakistan is that the country’s 4G pioneer Zongalso became the first company in the country to test 5G services in August 2019.
Telenor Pakistan is looking into bringing 5G to the country as well, but no dates have been released.
5G has been available in Saudi Arabia through Saudi Telecom Company (STC)since June 2019, but only in specific areas of major cities and only through home routers (no mobile option, yet).
According to the company’s CEO:
5G is considered as a very important step toward digitalization and connecting everything, which supports Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 toward economic diversification.
The 5G release in Saudi Arabia took place months after the company reached a deal with Ericsson to launch 5G in the country. STC has also partnered with Nokia to roll out 5G in Saudi Arabia; they announced in early 2019 that the rollout phase had already started.
Another 5G provider in Saudi Arabia is Zain. Over 20 locations have 5G availability, including Riyadh, Al Khobar, Dhahran, Tabuk, Hail, Sabya, Ahad Rafidah, Taif, Bisha, Najran, and Jaizan; see a 5G coverage map here. The Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G and ZTE Axon 10 Pro 5G are Zain’s 5G products.
5G in Bahrain arrived in July 2019 when STC (previously called VIVA) launched their 5G data plans. You can get mobile 5G from STC with one of their 5G phones, or 5G at home with the 5G router. The service is available in areas like Reef Island, Amwaj Islands, and Riffa Views.
Batelco is another company bringing 5G to Bahrain, choosing Ericsson to provide the 5G equipment. Availability is limited to just a few areas as of right now: Amwaj Islands and Reef Island.
5G in Kazakhstan isn’t coming as soon as other countries despite the fact that it’s the ninth-largest country in the world. However, according to Prime Minister Askar Mamin, 5G is definitely in sight, calling for an “Action Plan for the implementation of 5G in Kazakhstan.”
Askar Mamin said in a meeting held in May 2019, that 5G is expected to cover all Kazakhstan settlements that have a population greater than 50 thousand people.
In October 2019, the VEON telecom company launched a 5G trial on a live network.
The country’s second-largest mobile network operator, Mobitel, invested $50 million USD in 2019 to roll out 5G in Sri Lanka.
Mobitel has been working on bringing 5G to Sri Lanka for years. In early 2017, they partnered with Ericsson with the signing of the 5G Island of Innovation Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to bring 5G to Sri Lanka.
Service provider Smart Axiata will most likely be the first company to launch 5G in Cambodia. They were the first service provider to make 4G available in the country in 2014, and followed up in 2019 by showcasing the country’s first 5G live trial. The company expects the first few years of their 5G rollout in Cambodia to be focused on hotspots in major cities.
Viettel Cambodia (MetFone) is another company launching 5G service in Cambodia, in partnership with Telecom Cambodia.
Vodacom Group, which was the first to introduce 4G, 3G, and 2G in South Africa, is at it again with the release of a 5G trial in Lesotho in August 2018. They showcased a fixed wireless access (FWA) network using a temporary license in the 3.5 GHz band.
Vodacom’s 5G network should launch this year through the use of Liquid Telecom, which will provide nationwide 5G wholesale services to the market in early 2020.
Rain is another South African telecom that’s rolling out 5G. From November 11, 2019 and onward, Rain customers can access the 5G network from home in parts of Johannesburg and Tshwane, with more areas becoming available throughout 2020. Check 5G coverage in South Africa with the Rain coverage map.
MTN Group Limited partnered with Ericsson in November 2018, to deploy a fixed wireless access 5G site in Midrand. Although MTN South African hasn’t announced a 5G release date, the trials and tests they’ve performed shows that they’re interested in developing 5G applications and might one day offer customers a 5G network.
Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) plans 5G to roll out in 2020.
Tigo Senegal and Ericsson are working together to upgrade its network to roll out LTE across 1,000 sites. While this isn’t 5G service, it is an important stepping stone.
Although a 5G release date for Egypt isn’t yet known, Telecom Egypt and Nokia agreed in early 2019 to introduce a 5G network.
The telecom company Inwi, which covers over 90 percent of the country with mobile internet access, is bringing 5G to Morocco.
The two other licensed telecom companies in Morocco are Orange Morocco and Maroc Telecom, but both have been silent on a 5G deployment in the country.
The release date for 5G in the Congo is unclear, but according to Léon Juste Ibombo, the country’s minister of Posts, Telecommunications and Digital Economy, we know that the 5G rollout will involve Applus and Congo Telecom:
Investments in Congo’s telecommunications sector are astronomical and the state needs credible companies to help it implement the digital economy ecosystem. This company will help our incumbent operator, Congo Telecom, to implement 5G.
Ooredoo Tunisia has partnered with Nokia through the use of the company’s AirGile cloud-native core, to transition Ooredoo to a place where it can provide Tunisia customers with 5G.
Safaricom will likely launch 5G in Nairobi in early 2020.
5G networks are live right now in some European countries, and others will get 5G during 2020.
Telenor, the country’s biggest telecom operator, launched 5G in Norway in March, 2020, following early testing from 2017. These locations currently have access to the 5G network: Kongsberg, Elverum, Bodø, Askvoll, Fornebu, Kvitfjell, Longyearbyen and Spikersuppa in Oslo, and Trondheim.
Telia Company is another mobile network operator in Norway that opened its first 5G test network in December 2018. Their first trial partner was the Odeon movie theater in Oslo, marking the world’s first 5G cinema. Managing director of Telia Norway said in their December press release, “We are going to develop 5G-based solutions industry by industry, area by area.”
Telia Norway also partnered with Norwegian ISP Get to launch a 5G pilot in a family home, complete with smart tech from Futurehome. Get’s product director said “This family is far ahead of the rest of us, with a home filled with clever things connected through 5G. It is something the rest of us will not experience for several years, but it’s really fun to see what we will get with the latest technology.”
According to the 5G Strategy for Germany, released by Germany’s Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure (BMVI), trial installations began in 2018 with a commercial launch in 2020. 5G is planned to be rolled out “over the period to 2025.”
Deutsche Telekom rolled out 5G in Germany in Berlin, Darmstadt, Munich, Bonn, and Cologne in September 2019. Connectivity is possible through the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G, Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G, Huawei Mate 20 X 5G, and HTC 5G Hub. A total of at least 20 major German cities will have 5G by the end of 2020, and they plan to cover 90 percent of the country with 5G by 2025.
Another German telecom company that has launched 5G services in the country is Vodafone. They turned on their first 25 base stations on July 16, 2019, added Berlin a month later, and made it a goal to have 50 running before the end of August 2019. Customers can use 5G with the Huawei Mate 20 X 5G and Samsung Galaxy S10 5G.
Broadband telecom provider Telefónica Germany revealed in December 2018, that in collaboration with Nokia, they finished building their “Early 5G Innovation Cluster” in Berlin. It will be used to “test and measure the performance and coverage of first 5G services in a dense urban area.”
German ISP United Internet AG is another potential 5G player, having announced in early 2019 that they’d be taking part in a 5G spectrum auction.
Vodafone will provide 5G services to customers in Karlovy Vary by July 2020. This will come a full year after the company tested a 5G holographic call in the same city.
The UK’s largest network operator, EE, was the first to launch 5G in the UK on May 30, 2019. Service started in London, Cardiff, Edinburgh, Belfast, Birmingham, and Manchester, and the company now operates the 5G network in over 70 cities and towns.
EE was also the first in the world to offer the OnePlus 7 Pro 5G smartphone, but they also offer their customers the Samsung Galaxy S20 Ultra 5G, OPPO Reno 5G, LG V50 ThinQ, and other 5G phones. See their list of 5G phones for all of them.
Vodafone UK is another big mobile telecommunications provider in the UK. After testing how 5G can be used in car communications and successfully completing a holographic phone call using 5G, they launched their fifth-gen network in seven cities on July 3, bringing their total 5G coverage to 15 UK locations. The Vodafone 5G phones you can use on the network include the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G and Xiaomi Mi MIX 3 5G.
After announcing their commitment to invest billions in 5G, UK’s Three is another company that launched 5G in the UK, accessible first with Huawei’s 5G phone. After testing 5G for home use, the company also launched their 5G home broadband service on August 19 in London. Three has a list of everywhere you can get their mobile 5G in the UK.
BT Mobile launched 5G services in the UK on October 11, 2019, in 20 cities. See the 5G phones and plans you can get with BT Mobile.
O2 has a 5G network in the United Kingdom, too. It’s currently available in 20 locations, including London, Edinburgh, Cardiff, Belfast, Leeds, Slough, Leicester, Lisburn, Manchester, Birmingham, Glasgow, Liverpool, Newcastle, Bradford, Sheffield, Bristol, and other locations. There are several 5G phonesyou can use on the O2 5G network.
Tesco Mobile uses O2’s network and also began offering 5G to its customers in early 2020.
CityFibre and Arqiva are two more companies with 5G trials in London. They’re in the process of creating a “5G-ready network platform nationwide that will provide the best network at the best economics for Mobile Network Operators.”
Vodafone launched 5G in Italy in these five cities in June 2019: Naples, Bologna, Milan, Turin, and Rome. The company plans to roll out 5G to 100 cities by 2021. There are several 5G phones you can buy through Vodafone’s website.
TIM (Telecom Italia), the largest telecom provider in Italy, made 5G available in Naples, Rome, and Turin as of July 5, 2019. Their 5G network went live in another six cities before the start of 2020: Milan, Bologna, Verona, Florence, Matera, and Bari. By 2021, 120 towns and cities will be covered with TIM’s 5G network.
Iliad, in partnership with Nokia, will deploy 5G across Italy.
The first 5G network in Switzerland went live April 17, 2019, via Swisscom. It launched in 54 towns, including Basel, Bern, Chur, Davos, Geneva, Lausanne, and Zurich. According to Swisscom, more than 90 percent of the population is covered.
Swisscom currently offers the OPPO Reno 5G, LG V50 ThinQ 5G, and Samsung Galaxy S10 5G smartphones, but will have more available from other companies, such as Huawei, later in the year. These devices will work everywhere there’s 5G service from Swisscom, through their inOne mobile subscriptions.
The country’s second-largest telecommunications company, Sunrise, is also working to release 5G in Switzerland. They’ve already covered over 200 cities/villages with 5G, blanketing 80–98% of Dietikon, Bülach, Opfikon, Autafond, and other locations with 5G coverage. There’s a Sunrise 5G coverage map available, which also lists all the areas you can get Sunrise 5G service in Switzerland.
The company currently offers four 5G smartphones: Samsung Galaxy S10 5G, Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G, Huawei Mate 20 X 5G, and Xiaomi Mi MIX 3 5G. They also provide the HTC 5G Hub.
Sunrise ran an ultrafast, 3.28 Gbps 5G test in late 2017, erected their first 5G antenna in mid 2018, and then in November 2018, made live their first standardized 5G network at a ski resort.
Salt (formerly Orange Communications) is another telecom company planning 5G in Switzerland. They revealed in January 2019 that they selected Nokia to upgrade their radio and mobile core network to provide mobile 5G services.
Vodafone Spain was the first operator to launch 5G in Spain. On June 15, 5G became available to customers in these locations:
See if your specific address has 5G coverage with the Vodafone Mobile Coverage Map.
According to Vodafone, 5G speeds at launch can be up to 1 Gbps, but will increase to up to 2 Gbps before the end of the year. You need a 5G phone from Vodafone Spain to access the network.
After initially purchasing spectrum to implement 5G, Vodafone Spain launched 5G trials in various cities in June 2018, including Madrid, Valencia, Seville, and Barcelona. In late 2018, they installed a 5G network node in La Nave, Madrid, and in February 2019 used standards-based 5G phones to complete their first 5G video calls between Madrid and Barcelona.
Orange plans to launch 5G in Spain in 2020. The company revealed in early 2019 that they made their first 5G call using their next-gen network in Valencia and will continue testing the 5G technology in Seville, Vigo, Malaga, Barcelona, Bilbao, and other cities.
Network operator A1 kicked off their path toward 5G in Austria by making their first 5G data connection in Gmünd in early January 2019. See their 5G plans and phones here.
Magenta Telekom (previously called T-Mobile Austria) is deploying 5G mobile base stations across the country following a 110 MHz spectrum purchase in March 2019. In late March, the company revealed several of Austria’s 5G pioneers.
Hutchison Three Austria and ZTE are deploying 5G in Austria, too. Their first business client was in Linz, and with 20 5G sites set up by June 2019, it marked Austria’s first city with continuous 5G coverage.
The Elisa Oyj telecommunications company in Finland opened a commercial 5G network in Tampere in June 2018, claiming to be “first in world to launch commercial 5G.” According to their 5G coverage map, the network is also located in Oulu, Kuopio, Helsinki, Jyväskylä, and other areas.
Elisa has 5G Unlimited plans for 44.90 EUR /month at 1 Gbps and 34.90 EUR /month at 600 Mbps. The ZTE Axon 10 Pro 5G phone can be used on Elisa’s 5G network.
Telia revealed in early December 2018, that Helsinki Airport became the first 5G airport in the world and their first customer using their pre-commercial 5G network. In early 2019, the company began commercial use of its 5G network in three cities and has since expanded to include several more. See the Telia 5G devices you can buy right now for mobile and FWA 5G access.
DNA is another Finnish telecommunications company bringing 5G to Finland. They began offering fixed wireless access service in December, 2019. However, the company says that even with the introduction of 5G, 4G will remain the primary network technology used by most people.
In 2018, Russia’s largest mobile operator, Mobile TeleSystems (MTS), partnered with Samsung to run various 5G tests that included video calls, ultra-low latency video games, and 4K video streaming.
These 5G tests were performed to show that not only is 5G coming to Russia but that Samsung’s 5G routers, tablets, and other devices are fully capable of running on a 5G network.
According to GSMA, 5G networks will cover over 80 percent of the Russian population by 2025, so it can be assumed that a big portion of the country will have access even sooner.
Another indicator that 5G in Russia is coming sooner than later is the 5G research center that’s open in Innopolis, a high-tech city in the Republic of Tatarstan.
Tele2 Russia is another telecom company bringing 5G to Russia. In collaboration with Ericsson, the company announced in February 2019 that they’d deploy 50,000 base stations in Russia. However, Tele2’s CEO says “Before launching 5G networks, Russia must first address several infrastructure issues.”, so customers might have to wait a while to receive 5G services.
Orange is currently the only European telecommunications company that has announced 5G plans for Luxembourg.
It’s unclear when 5G is coming to Slovakia, but mobile operator SWAN Mobilesigned a 5G commercial contract with ZTE in early 2019 to kick off 5G rollout plans. In July 2019, the two performed the the country’s first 5G video call.
In early 2020, Orange Slovensko selected Nokia to prepare its Radio Access Network for 5G.
The telecom giant Vodafone went live with a 5G network in Cork, Dublin, Galway, Limerick, and Waterford on August 13, 2019.
eir’s 5G network is live as well. Its launch locations included Dublin, Limerick, Kilkenny, Waterford, Cork, Galway, Dundalk, and more. There’s an eir 5G coverage map with all the locations.
Vodafone is also working on fixed wireless access. In early December 2018, the company announced that they would begin trials for rural 5G broadband in Roscommon, Gorey, Dungarvan, and Clonmel, covering 20,000 premises.
Imagine is another telecom bringing 5G to Ireland. They announced the launch of their 5G-ready fixed broadband network in February 2019 and plan to build out over 300 sites to cover over one million premises by the fall of 2020.
CEO Sean Bolger had this to say about their 5G plan:
As an Irish company, we are delighted to announce this significant investment and a new approach which will finally solve this problem and deliver much needed, fast and reliable high-speed broadband to homes, businesses and communities across regional and rural Ireland, today and into the future.
Three Ireland is launching a 5G network in the country, too, but it’s not clear when.
Føroya Tele, the Faroe Islands’ largest telecom provider, launched 5G on June 6, 2019.
Jersey Telecom (JT) and ZTE have announced that 5G is coming to the Channel Islands. They began a pre-commercial launch in mid-2019 to test 5G.
5G is being tested in the capital, Minsk, via beCloud.
The Romanian government approved the 5G Strategy in June of 2019.
The 5G Strategy for Romania projects an action plan with concrete tasks and deadlines for deployment, targeting the launch of services in 2020 and 5G service coverage of all urban centers and major land transport routes by 2025.
On June 26 2019, Vodafone Romania launched the country’s first 5G subscriptions. All the details, and the 5G phones you can buy, are available on their Supernet 5G page.
RCS & RDS is the largest Romanian cable and satellite TV company, and they also have 5G available through the Digi Mobil 5G Smart network.
Orange launched 5G in Romania in November 2019. Coverage started in Bucharest, Cluj-Napoca, and Iasi, and will reach more areas throughout 2020. See the Orange 5G coverage map for details.
Magyar Telekom, the largest Hungarian telecom company, launched 5G in Hungary in April 2020. Service began in parts of Budapest and Zalaegerszeg.
Vodafone is another company launching 5G in Hungary. In May of 2019, Vodafone launched Hungary’s first live 5G station in Zalaegerszeg.
Commercial 5G services are expected to come to Croatia by the end of 2020. Service will start in Osijek, within the region of Slavonia.
Telia Company is planning a commercial launch of 5G in Sweden in 2020.
In late December 2018, in collaboration with Ericsson and KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Telia launched a 5G testbed in Stockholm to experiment with 5G applications.
In early 2019, in collaboration with Volvo CE and Ericsson, Telia erected a 5G network in Eskilstuna with the primary focus being industrial use, such as remote-controlled machines.
A Tele2 5G network is coming to Sweden as well. They plan on providing access in 2020, but confirms that it’ll take a few years before the majority of people will have high-speed access.
Polish mobile phone network T-Mobile Polska announced on December 7, 2018, the launch of the country’s first 5G network. It’s currently available only in the center of Warsaw via five base stations, but T-Mobile plans to develop 5G in other locations to reach the entire country.
According to T-Mobile,
Devices providing access to the network have been distributed to selected T‑Mobile partners, so they can be used in order to develop new business solutions and products, which will be eventually offered on the mass market.
Orange is another European mobile network operator that will launch 5G in Poland, but it won’t have a commercially available network up and running until 2020 or 2021.
Polkomtel’s Plus mobile phone network operator is rolling out 5G in Poland in 2020 with Ericsson’s 5G technology. The network will initially be deployed across Warsaw, Gdańsk, Katowice, Łódź, Poznań, Szczecin, and Wrocław.
Vodafone brought Portugal its first 5G connection on December 12, 2018, via a 5G smartphone prototype from Qualcomm. The company also tested a virtual reality game and video call on Ericsson’s 5G network.
ANACOM, Portugal’s communications regulator, will hold a 5G spectrum auction in June 2020 and expects commercial rollouts before 2021.
French regulator Arcep expects commercial 5G rollout in France to take place in 2020.
Orange has launched 5G pilots in France in Lille, Douai, Marseille, and Châtillon.
Iliad, in partnership with Nokia, will deploy 5G across France.
Estonia will likely see a commercially available 5G network in 2020.
The country’s first 5G test network went live on December 20, 2018. It was launched by Telia Company, TalTech University, and Ericsson.
According to Telia Company, the 5G network is a…
testbed for innovation and research for industry partners and academia. TalTech University´s scientists and students, as well as companies and startups can create and test solutions that require fast, high-quality data connection.
One company bringing 5G to Latvia is Tele2. They launched their first 5G base station in Riga in July of 2019, made their first 5G video call a few months later, have released 5G phones, and began offering their 5G network in Daugavpils and Jelgava in early 2020.
Telenor Group brought 5G tests to Denmark in 2019 via Nokia’s AirScale Base Stations.
According to Telenor, the trials:
support 5G use cases such as robotics control, industrial automation, 5G/LTE dual connectivity and Fixed Wireless Access for high performance last mile connectivity.
Telia Company is another mobile network operator that began live 5G tests in Denmark in June 2019.
Mobile telecom company Azercell is planning to launch 5G in Azerbaijan. In early 2019, the company chose Ericsson in a two-year 5G deal to provide the telecom company with radio equipment and related services.
Síminn is the leading provider of wireless communication services in Iceland. They announced in early 2019 that they’d be partnering with Ericsson to deploy 5G-ready equipment to the country.
T-Mobile is promising nationwide 5G coverage in the Netherlands in 2020. In the summer of 2019, T-Mobile announced the launch of three 5G research locations: Scheveningen, The Hague Tech, and the T-Mobile head office in The Hague.
Monaco Telecom customers have access to 5G across all of the Principality of Monaco via the Huawei Mate 20 X and the Xiaomi Mi MIX 3. Full coverage of the entire country was completed in July 2019.
Proximus is the largest mobile telecommunications company in Belgium. Take a look at the Proximus 5G network coverage map for all the details on where you can get 5G in Belgium. You’ll need a 5G mobile subscription as well as a 5G phone that works on the Proximus network, such as the Oppo Find X2 Pro 5G.
In 2019, Orange and Proximus agreed to set up a shared mobile access network, a move that could mean 5G reaches across Belgium even faster.
Vodafone Malta doesn’t have a solid 5G release date yet, but they’re working on bringing 5G to Malta. On October 4, 2019, Vodafone Malta began letting customers try out 5G in areas of Birkirkara, St Julians, and Sliema.
Most major countries in Oceania saw limited 5G roll-out in 2019 with greater availability arriving in 2020.
Australia’s second largest telecommunications company, Optus, launched 5G for mobile and home use on November 4, 2019. The launch involved over 290 5G sites in Sydney, Canberra, Adelaide, Brisbane, Melbourne, Perth, and other locations in NSW, Victoria, and Queensland. See the Optus 5G coverage mapfor details.
Telstra announced in August 2018, that they had enabled 5G technology in areas of the Gold Coast, giving the state of Queensland the country’s first 5G-ready network. They also enabled 5G mobile base stations in Adelaide, Canberra, and Perth in October 2018, and in Melbourne and Sydney in December. According to the CEO, Telstra erected 200+ 5G-capable sites before the end of 2018.
In November 2018, Telstra confirmed that they completed Australia’s very first 5G connection on a live network. The company’s Network Engineering Executive said that they will “continue testing over the coming months to improve data rates and overall performance in readiness for device availability.”
In December 2018, Telstra revealed that their first customer using a 5G device — the HTC 5G Hub — was FKG Group in Toowoomba.
Vodafone has provided a 2020 release date for 5G in Australia. This is a reasonable time frame considering that not only is Vodafone the country’s largest mobile provider but because they partnered with Nokia in 2019 to agree to a 2020 5G rollout. Vodafone users can expect 5G in these areas.
According to Kris Faafoi, New Zealand’s Minister of Broadcasting, Communication and Digital Media,
First allocation of 5G spectrum will be the 3.5 GHz band, with national rights to this portion of the spectrum expected to be auctioned early in 2020.
Having already been laying the groundwork for 5G, and implementing 5G trials in March of 2018, New Zealand’s Spark NZ plans to have a full 5G network ready to go in 2020. They switched on 5G for the first time in September 2019for a limited number of customers, and launched 5G in five other towns in December, 2019.
Vodafone is another 5G player in New Zealand. They switched on 5G in parts of Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, and Queenstown on December 10, 2019. See Vodafone New Zealand’s 5G-ready phones.
5G fixed wireless access arrived in Guam in the second half of 2019 through SK Telecom and IT&E.
According to SK Telecom, the plan has been to start the 5G rollout in Guam in “highly concentrated central areas of cities, local business customers and areas that lack fixed-line infrastructure.” Coverage will then extend to wider areas.
Source: Lifewire
If a cell phone comes in close contact with someone who might have the virus, the user receives a text message informing them and then instructing them to self-quarantine for 14 days.
However, the quarantine is not necessarily voluntary, depending on where you live. In some countries, phones have been used as a sort of house arrest ankle-bracelet that will notify authorities if the person being monitored leaves the house for any reason.
These apps are being touted as the way to end the shut down in both Italy and the UK and it appears that officials are going to be taking things in that direction.
At face value, it may appear that this could be a useful strategy in preventing the spread of disease, but privacy advocates and tech experts are concerned that this information could be misused and that the unprecedented surveillance capabilities could be kept and held by corrupt governments long after the pandemic is over.
In a recent interview with Vice, NSA whistleblower Edward Snowden expressed his concerns about the coming surveillance program, calling it the “architecture of oppression.”
“Do you truly believe that when the first wave, this second wave, the 16th wave of the coronavirus is a long-forgotten memory, that these capabilities will not be kept? That these datasets will not be kept? No matter how it is being used, what’ is being built is the architecture of oppression,” Snowden said.
Snowden recognized that the virus was a serious threat and said that the intelligence community was well aware that it was only a matter of time before a massive pandemic crippled the country, even back when he was working in the NSA.
“There is nothing more foreseeable as a public health crisis in a world where we are just living on top of each other in crowded and polluted cities, than a pandemic. And every academic, every researcher who’s looked at this knew this was coming. And in fact, even intelligence agencies, I can tell you firsthand, because they used to read the reports had been planning for pandemics,” he said.
Snowden questioned the positive numbers that have come out of China in recent weeks and pointed out that the Chinese government has been credited with reducing the spread of the illness because they took such draconian measures during the lockdown.
Perhaps their extreme strategy is not working as well as they say it is, but since the government maintained tight control of any information coming out of the country, it is impossible to say for sure.
“If you’re looking at countries like China, where cases seem to have leveled off, how much can we trust that those numbers are actually true? I don’t think we can. Particularly, we see the Chinese government recently working to expel Western journalists at precisely this moment where we need credible independent warnings in this region,” Snowden said.
In a statement published on Friday, Apple and Google announced that they were teaming up in a rare partnership to develop compatible contact tracing apps, which they claim will work on an “opt-in” basis.
However, according to Bloomberg, the companies are planning to eventually build the contact tracing into the device’s updates.
Apple and Google insist that you will still be able to opt-out of the program if you don’t want to participate, but it is possible that rankings on these apps could be used to gain entry into grocery stores or larger businesses and events once the economy opens up again.
“As authoritarianism spreads, as emergency laws proliferate, as we sacrifice our rights, we also sacrifice our capability to arrest the slide into a less liberal and less free world,” Snowden warned.
Source: The Mind Unleashed
 By A. Naran
By A. Naran
Conclusion: Wireless devices are harmful to human health. For now, wireless technologies must be avoided as much as possible.
“People should be made aware that the EMR from using day to day cellular, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth devices are harmful to human health. The levels of radiation observed in most cases such as phone calls, internet browsing on laptops and smartphones, using wireless routers and hotspots, Bluetooth smartwatches and smartphones are unsafe when compared with radiation limits determined by medical bodies. According to the current medical literature, various adverse health effects from exposure to RF EMR have been well documented. New and innovative wired solutions which provide the same level of user-friendliness should be encouraged.”
Note: This is a review article about the science on this issue. It is important because it was published in the IEEE journal. The IEEE is the international organization of engineers. The current FCC obsolete guidelines are based on the IEEE recommended guidelines which are thermally based i.e., they are based on the false assumption that unless the radiation changes the temperature in tissue, it is not harmful.
That may be good physics but it is bad biology. When the FCC wanted to adopt the IEEE guidelines, all the health agencies wrote letters objecting the guidelines. Some of them criticized the use of engineers’ recommendations for biological effects when they didn’t even have one medical professional on the committee that developed the guidelines.
Johnny Liberty, Editor’s Notes: Why Destroy the Global Economic System During the Coronavirus Crisis (and replace it with another that better serves the Global Power Structure)?
Source: London Real & YouTube
Source: YouTube
Editor’s Note: This is yet another tragic example of the unleashing of a new technology which has not been properly tested before deployment. Are these technology corporations so out of touch with their own humanity they do not consider the consequences beyond their own bottom line? 5G could very well be an end game for the human beings who cannot adapt to such high-levels of EMF in the environment and an extinction level event for many other creatures as well.
In a recently published article entitled, We Have No Reason to Believe 5G is Safe, Scientific American (SciAm) magazine issued a stern warning about the known and potential dangers of 5G technology.
Of particular significance is the fact that SciAm is the oldest continuously published monthly magazine in the United States, founded by inventor and publisher Rufus M. Porter in 1845, and running monthly since 1921. It is a highly influential publication, widely reputed for its rigorous scientific standards, and lauded by today’s fact-checkers as highly credible and staunchly pro-science.
In the article, University of California, Berkeley public health researcher Joel M. Moskowitz argues that 5G, along with previous w-fi and cellular technology, is much more harmful than the government and telecomm industry wants the public to believe.
His primary concerns center around a recent FCC announcement, made in a press release, that the FCC is close to reaffirming the radio frequency radiation (RFR) exposure limits that were previously adopted by the commission in the 1990’s… well before the introduction of 5G, 4G, 3G, 2G or even WiFi.
In short, the safety standards that the FCC wishes to maintain are severely outdated and fail to reflect the growing body of scientific evidence demonstrating harm.
Moskowitz notes that the ’90’s exposure limits only address the singular concern over the potential effects of the intensity of exposure to RFR. With the research we now have available the health concerns are much broader, including a sincere risk of cancer, among other things.
Moskowitz also cites the the International EMF Scientist Appeal, which elaborates on the now-known dangerous effects of RFR:
Moskowitz points out that,”the scientists who signed this appeal arguably constitute the majority of experts on the effects of nonionizing radiation. They have published more than 2,000 papers and letters on EMF in professional journals.” Inviting readers and policy makers to consider the weight of more than 500 peer-reviewed research studies finding, “harmful biologic or health effects from exposure to RFR at intensities too low to cause significant heating,” Moskowitz believes that more rigorous studies are necessary before the rollout goes forward.
In other words, the scientific jury is already out on the harmful effects of RFR, and the FCC is flat-out derelict in its duty to put public safety above telecomm industry interests.
Regarding the propaganda dimension of this debate, Moskowitz addresses the fact that industry spokepersons and related government officials frequently refer to contrarian viewpoints as ‘fear-mongering,’ pointing out that the current scientific research is legitimate, leaving the scientific community with a genuine responsibility to speak out about these concerns.
Cracks are showing in the government and telecom industry’s blanket assertion that 5G is safe, and many prominent and influential scientists, dignitaries, and organizations are now speaking out against 5G – the global human experiment without consent. For the editorial board of Scientific American to run a piece this condemning 5G is a very strong signal that even the most mainstream elements of the scientific community are genuinely concerned.
Terence Newton is a staff writer for WakingTimes.com, interested primarily with issues related to science, the human mind, and human consciousness.
This article (Scientific American, the Oldest US Monthly Magazine, Issues Severe Warning on 5G) was originally created and published by Waking Times and is published here under a Creative Commons license with attribution to Terence Newton and WakingTimes.com. It may be re-posted freely with proper attribution, author bio, and this copyright statement.
Source: Waking Times