Source: YouTube
Unmasked: Have we uncovered the truth about the 2020 election? | Pure Data
Source: YouTube
Source: YouTube

Author’s Note: Five months of intensive research, collating 670 research and news sources, are compacted in this succinct, readable and entertaining 167-page compendium about the “pandemic”. It provides a comprehensive overview for those with an open mind, still willing to learn, to expand perspectives far beyond media tidbits. This is the Dawning of the Corona Age.
May we remove our masks – and blindfolds – to take notice of what is actually rapidly happening around us to navigate how we can still “live free in an unfree world”.
This newly released book is dedicated to You. Thank you for educating yourself, “thinking twice before you think”, calmly sharing your insights, acting wisely and thereby reclaiming authority over your life! Enjoy the first chapter of thirty-two below.
“A compelling exploration far beyond the immediate impacts of the “pandemic”, Dawning of the Corona Age imagines how our human world may be altered long into an uncertain future. “
$10 PDF ORDER LINK: https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted_button_id=H7ZVUNGC58QE2
$25 PRINT ORDER LINK: https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted_button_id=QCQQL3JUTVURE (includes PDF Version with 670 Live Links)
$25 AMAZON PRINT ORDER LINK: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B08FSR3NJG
 1. Preface & Introduction
1. Preface & IntroductionLike a television series straight out of science fiction films, such as, V for Vendetta, Pandemic and The Matrix, the mainstream media narrative relentlessly broadcast at “We the People” seemed at first as surreal and as strange as an episode of The Twilight Zone.
Now, suddenly, and apparently without warning, we are living in a strange hybrid between George Orwell’s novel 1984, Aldous Huxley’s Brave New World and The Matrix. Science fiction has now become real.
George Orwell wisely observed that, “The further a society drifts from the truth, the more it will hate those that speak it.” In 1958, Aldous Huxley warned that, “Pharmacology and propaganda will make the masses love their slavery. As the world is forced into accepting greater and greater levels of government control in all areas of life, remember that nothing in politics happens by chance. There is a science to creating empires.”
 As the lead character Orpheus revealed in The Matrix film, “The Matrix is everywhere. It is all around us, even now in this very room. You can see it when you look out your window, or when you turn on your television. You can feel it when you go to work, when you go to church, when you pay your taxes. It is the world that has been pulled over your eyes to blind you from the truth.”
As the lead character Orpheus revealed in The Matrix film, “The Matrix is everywhere. It is all around us, even now in this very room. You can see it when you look out your window, or when you turn on your television. You can feel it when you go to work, when you go to church, when you pay your taxes. It is the world that has been pulled over your eyes to blind you from the truth.”
These perspectives reflect a deeper sense of what may be happening in our world today. For those open-minded enough to consider the truth as more important than convention and its lies, that sobriety is more essential than distorted states of consciousness, that the Earth and all of its natural wonders are more beautiful than any virtual reality, this book may just break open the possibility of a transformation of our understanding of this “pandemic”.
In truth, this may be the “crowning” of a “new age” of consciousness emerging from the rubble of an old world dying around us. A “Corona” age may very well be on the horizon if we act from a higher understanding of our own existence as true human beings instead of from our limited perspectives of material existence.
 For those with the courage to question authority, to question even our present sense of reality, this book is for you.
For those with the courage to question authority, to question even our present sense of reality, this book is for you.
“Do not believe in what you have heard; do not blindly believe in traditions just because they have been handed down for many generations; do not believe in anything just because it is rumored and spoken by many; do not believe merely because a written statement of some old sage is produced; do not believe in conjectures; do not believe in that as truth to which you have become attached from habit; do not believe merely
the authority of your teachers and elders,
or news sources or books.
Question all authorities and truisms.
Decide for yourself what is the veracity of your perceptions.
Ponder what is not true. Even more so, ponder what is true, deeply and continuously.”
~ Buddha
$10 PDF ORDER LINK: https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted_button_id=H7ZVUNGC58QE2
$25 PRINT ORDER LINK: https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_s-xclick&hosted_button_id=QCQQL3JUTVURE (includes PDF Version with 670 Live Links)
$25 AMAZON PRINT ORDER LINK: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B08FSR3NJG
 Preface and Introduction (PDF)
Preface and Introduction (PDF) International, National & State Declarations of Emergency
International, National & State Declarations of Emergency Dawning of the Corona Age
Dawning of the Corona AgeAPPENDIX
 By Raul Diego
By Raul Diego
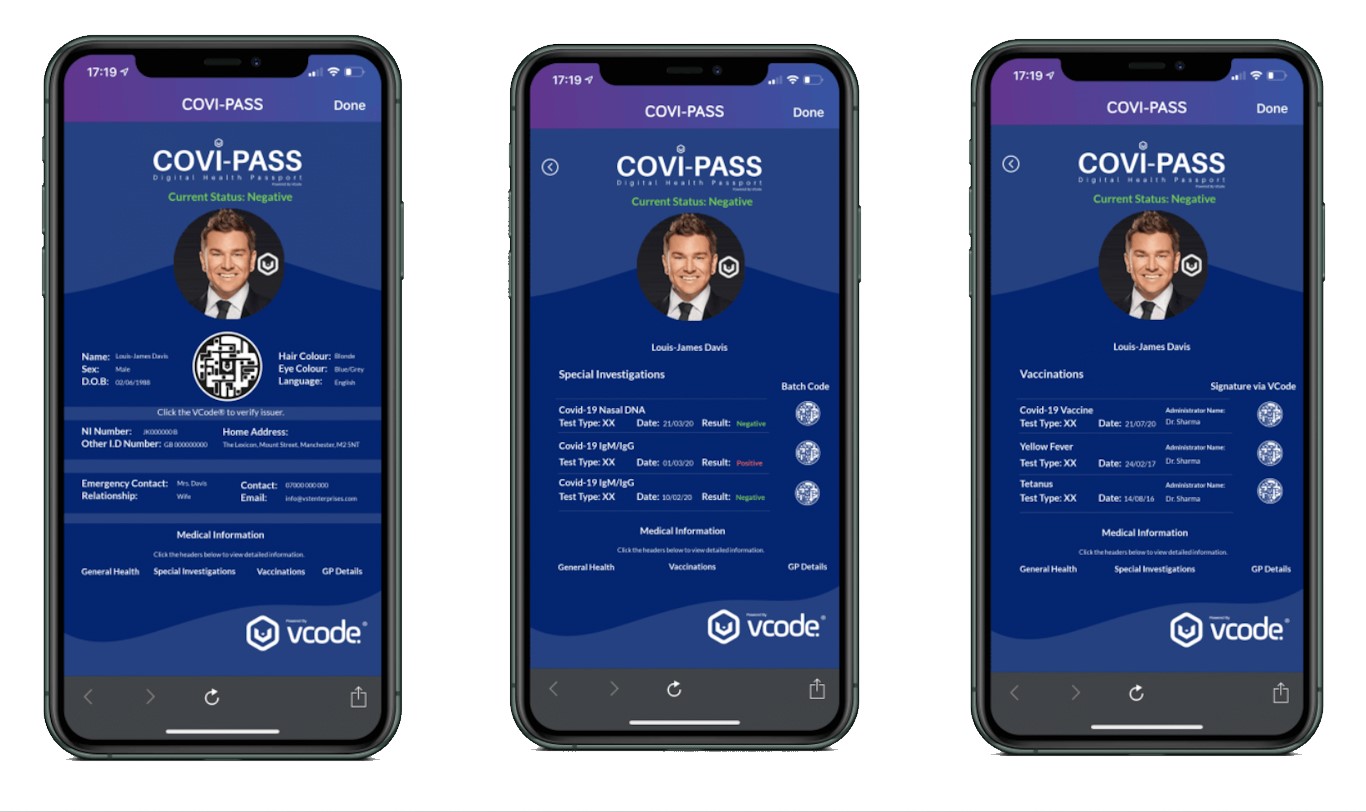
Editor’s Note: COVI-PASS will determine whether you can go to a restaurant, if you need a medical test, or are due for a talking-to by authorities in a post-COVID world. Consent is voluntary, but enforcement will be compulsory.
Through the magic of Internet meme culture, most Millennials will be familiar with the famous opening scene of the 1942 film, “Casablanca,” where two policemen stop a civilian in the “old Moorish section” of Nazi-occupied French Morocco and ask him for his “papers.” The subject is taken away at once after failing to produce the required documents. The cinematic exchange has been used ever since as a popular reference to the ever-encroaching hand of the state, which is now on the verge of attaining a level of control over people’s movements that puts the crude Nazi methods to shame.
A British cybersecurity company, in partnership with several tech firms, is rolling out the COVI-PASS in 15 countries across the world; a “digital health passport” that will contain your COVID-19 test history and other “relevant health information.” According to the company website, the passport’s objective is “to safely return to work” and resume “social interactions” by providing authorities with “up-to-date and authenticated health information.”
These objectives mirror those that Bill Gates has been promoting since the start of the COVID-19 lockdown. In an essay written by Gates in April, the software geek-cum-philanthropist lays out his support for the draconian measures taken in response to the virus and, like an old-timey mob boss, suggests the solutions to this deliberately imposed problem. Ironically, Gates begins to make his case for the adoption of mass tracking and surveillance technology in the U.S. by saying that “For now, the United States can follow Germany’s example”; He then touts the advantages of the “voluntary adoption of digital tools” so we can “remember where [we] have been” and can “choose to share it with whoever comes to interview you about your contacts.”
Gates goes on to predict that the ability to attend public events in the near future will depend on the discovery of an effective treatment. But he remains pessimistic that any such cure will be good enough in the short term to make people “feel safe to go out again.” These warnings by the multi-billionaire dovetail perfectly with the stated purposes of the aforementioned COVI-PASS, whose development is also being carried out in partnership with Redstrike Group – a sports marketing consultancy firm that is working with England’s Premier League and their Project Restart to parse ticket sales and only make them available to people who have tested negative for the virus.
VST Enterprises Ltd (VSTE) is led by 31-year old entrepreneur, Louis-James Davis, who very recently stepped down from a “science & technology ambassadorship” in the African nation of Zimbabwe to focus on the company’s role in the UN’s SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) Collaboratory initiative, comprising a series of “cyber technology projects across all 193 member states of the United Nations.”
These will use the same proprietary VCode and VPlatform technologies underpinning the COVI-PASS that will reportedly tackle issues such as illegal mining and counterfeiting. This “third generation” barcode technology overcomes the limitations of older “second generation” versions like QR-codes, according to Davis. “Data and sensitive information scanned or stored in either a QR code and barcode can be hacked and are inherently insecure,” Davis claims, “leaving data and personal details to be compromised.” These, and other flaws of the prevailing “proximity apps” were exploited by VST Enterprises to position itself to land large government and private sector contracts.
By all measures, the strategy has proven wildly successful and VST now enjoys strong favor in the highest circles of the UK government as evidenced by the ringing endorsement of former Prime Minister Theresa May, prominently displayed on the COVI-PASS website. More practically, VST now has a direct partnership with the UK government and has secured contracts to deploy its technology in 15 countries, including Italy, Portugal, France, India, the US, Canada, Sweden, Spain, South Africa, Mexico, United Arab Emirates and the Netherlands.
In May, VST signed a deal with international digital health technology firm and owner of COVI-PASS, Circle Pass Enterprises (CPE) to integrate VST’s VCode into the biometric RFID-enabled “passports” which can be accessed via mobile phone or a key fob will flash colored lights to denote if an individual has tested negative, positive or is to be denied entry to public locations. Awarded the ‘Seal of Excellence’ by the EU, VCode® technology will ensure that all of our most sensitive personal and health information can be accessed by authorities at a distance, dispensing with messy and potentially dangerous face-to-face encounters with police or other enforcement personnel.
So far, the concerns over the digital health passport’s threat to freedom and privacy have been lukewarm at best and it seems as if the world has already accepted that full-fledged population control methods such as these will simply be a fact of life. While the coronavirus pandemic has certainly done much to bring the public over to this way of thinking, the campaign to normalize this sort of Orwellian power-grab has been ongoing for many years and Bill Gates – who many media outlets have whitewashed out of stories related to these measures – has been at the forefront of its promotion.
The Innovation for Uptake, Scale and Equity in Immunisation (INFUSE) project was launched in Davos, Switzerland in 2016. The program was developed by an organization funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation called GAVI (The Vaccine Alliance), which has been calling for a digital health ID for children along with partners in the broader !D2020 initiative like the Rockefeller Foundation and Microsoft.
In a recent interview, the deputy director of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Hassan Damluji, derided the idea that the COVID-19 pandemic was in any way subsiding and even warned that, far from receding, the pandemic was “deep into wave three.” His remarks were specifically targeted to the very regions he oversees for the foundation, which include the Middle East and parts of Asia, which he stressed would be the focus of the next wave. Damluji was “most recently involved in a five-year fundraising cycle for GAVI,” an effort led by Saudi Arabia, whose investment he praised as a powerful “signal [that] others had an obligation to follow.”
Gates concludes his editorial with a comparison to World War II, stating that said conflict was a “defining moment of our parents’ generation” as the COVID-19 pandemic is to ours, implying that the changes taking place now are akin to the Allied forces’ defeat of the Third Reich. Except, of course, that immunity passports or digital health certificates sound exactly like what Hitler wished for the most. After all, wasn’t the idea of a superior race based on considerations of superior health and vitality over the ostensibly sick and unfit? Hard to argue against the idea that a universal health passport is nothing less than the ultimate fulfillment of that dystopian nightmare.
Feature photo | Salt Lake County Health Department public health nurse Lee Cherie Booth performs a coronavirus test outside the Salt Lake County Health Department in Salt Lake City, May 20, 2020. Rick Bowmer | AP
Raul Diego is a MintPress News Staff Writer, independent photojournalist, researcher, writer and documentary filmmaker.
Source: Mint Press News
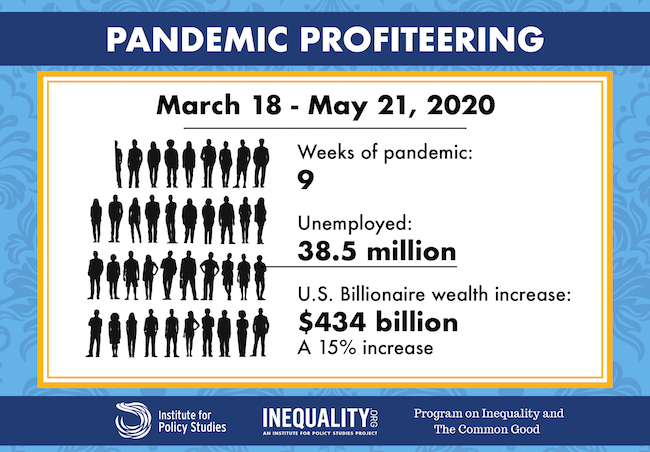
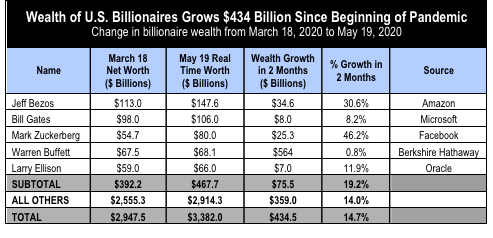
The number of U.S. citizens filing for unemployment increased to 38.6 million since March 18, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Over the same two months, the wealth of U.S. billionaires has surged $434 billion – an increase of 15 percent.
The combined fortunes of Jeff Bezos and Mark Zuckerberg alone grew by nearly $60 billion during these two months, according to a new analysis, jointly released by Americans for Tax Fairness and the Institute for Policy Studies, which released Billionaire Bonanza 2020 in April to examine billionaire wealth during the first month of the pandemic.
Between March 18 and May 19, the total net worth of the 600-plus U.S. billionaires rose from $2.948 trillion to $3.382 trillion. In March, there were 614 billionaires on the Forbes list. There are 630 two months later, including newcomer Kanye West at $1.3 billion.
Among other COVID-19 victims are the more than 16 million Americans who have likely lost employer-provided healthcare coverage. Low-wage workers, people of color and women have suffered disproportionately in the combined medical and economic crises. Billionaires are overwhelmingly white men.
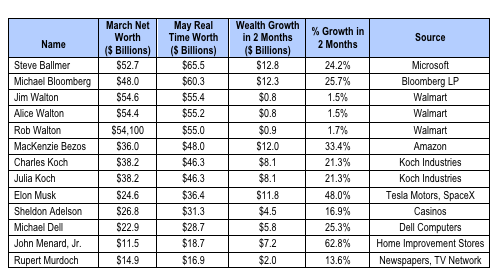
Wealth growth of other select billionaires in the top 30 on the Forbes May 19 list are below.
Download our social media toolkit here.
Sources: All data analyzed by ATF and IPS is from Forbes and available here.
March 18, 2020, data is from the Forbes World’s Billionaires List: The Richest in 2020.
May 19, 2020 data was taken from Forbes real-time estimates of worth that day.
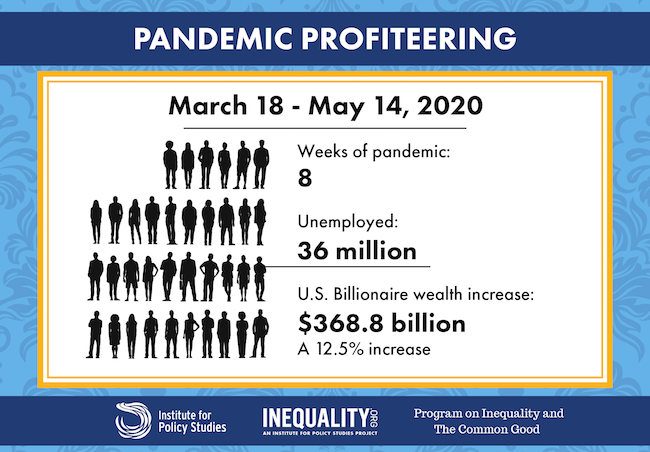
Between March 18 and May 14, 2020, over 36 million U.S. workers lost their jobs, with 2.98 million claims in today’s announcement. Over these same eight weeks, U.S. billionaires saw their wealth increase by $368.8 billion, a 12.51 percent increase.
On March 18th, U.S. billionaires had a combined $2.947 trillion, down from $3.111 trillion a year earlier, according to Forbes annual global billionaire survey. As of May 14, total U.S. billionaire wealth has increased to $3.316 trillion. In the last eight weeks, 14 new billionaires joined the U.S. billionaire list, which increased from 614 to 628.
Even with a decline in markets, Elon Musk’s wealth increased $3.5 billion in the last week, since May 6. Jeff Bezos’ wealth increased by $900 million and Eric Yuan saw his wealth increase by $800 million. Mike Bloomberg saw his wealth increase by $400 million.
Between March 18, when Forbes published their 2020 annual Global Billionaire Survey, and the morning of Thursday, May 14, these billionaires have seen their wealth surge:
Read more about IPS’s methodology in our report and in this fact check by USA Today.

Between March 18 and April 30, 2020, over 30 million U.S. workers lost their jobs. Over these same weeks, U.S. billionaires saw their wealth increase $406 billion, an increase in 13.8 percent increase.
On March 18th, U.S. billionaires had a combined $2.947 trillion, down from $3.111 trillion a year earlier, according to Forbes annual global billionaire issue.
As of April 29, total U.S. billionaire wealth had increased to $3.353 trillion. This is a boost of $406.2 billion, a 13.78 percent increase in six weeks.
Between April 22 and April 29, billionaire wealth increased $98.1 billion, a 3 percent increase.
Our Billionaire Bonanza 2020 report has struck a nerve around the world with over 200 media stories in U.S. and global press. See the full report, Billionaire Bonanza 2020: Wealth Windfalls, Tumbling Taxes, and Pandemic Profiteers
Highlights of coverage include: Reuters, Newsweek, New York Post, The New York Times, Washington Post, Fox News, Investing.com, Nasdaq, GQ, US News & World Report, Fortune, The Week, Business Insider , Futurism, Bill Moyers.com, LA Progressive. In These Times, Yahoo Finance, Gizmondo, and GQ Magazine, and Jacobin.
Several feature pieces include:
Fast Company, “American Billionaires Have Gotten $280 billion richer since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic,”
Capital & Main: “Tale of Two Pandemics: The Rich Are Getting Richer”
Sunday Guardian (UK): “Heads we win, tails you lose; America’s rich have turned pandemic into profit.”
Business Insider did four different stories, including: “9 mind-blowing facts about America’s richest people”.
New Republic, “Billionaires Are Eating the Economy,” May 7, 2020
We were fact-checked as true by USA Today, which resulted in one of the best stories about our methodology. See: USA Today: Molly Stellino, “Fact Check: The super rich did indeed get richer in early weeks of coronavirus pandemic,” May 7, 2020.
Billionaire Bonanza made a splash in the sports reporting world, including this story in Football Times, “Arsenal owner Stan Kroenke’s wealth increases by £323m as players take wage cut”, May 6, 2020. James Benge wrote, “ The wealth of Arsenal owner Stan Kroenke has increased by over £300million since the start of 2020, a study by a leading American think tank has revealed.”
Sample of international coverage: Straits Times (Singapore) Observador (Portugal), Daily Mail (Australia), Regina Leader Post (Saskatchewa, Canada), Sunday Times(South Africa) “Corona boost for richest in the U.S.” International Business Times. La Jornada (Mexico), Publico (Spain),
Our own commentaries appeared in CNN and The Guardian. An op-ed by report co-authors, Omar Ocampo and Chuck Collins, “Rich Getting Richer Despite Pandemic,” has been syndicated in over 60 U.S. newspapers by the Tribune News Service/ Progressive Media Project, including in Houma Today (LA), Daily Comet (Lafayette, LA), Tyler Paper (TX) The Derrick (Oil City, PA), Bozeman Daily Chronicle (MT).
Source: Inequality
 The interactive Ookla 5G Map tracks 5G rollouts in cities across the globe. Updated weekly from verified public sources and Ookla data, you can follow operators’ newest 5G networks on @Ookla5GMap. Click above graphic to go to the interactive map…
The interactive Ookla 5G Map tracks 5G rollouts in cities across the globe. Updated weekly from verified public sources and Ookla data, you can follow operators’ newest 5G networks on @Ookla5GMap. Click above graphic to go to the interactive map…
Source: Speedtest
 By Denise Minger
By Denise Minger
Long time no blog, fam!
So, I had this hope that the next thing I posted here would be a grand explanation about my extended absence, all the weird stuff that’s happened over the past few years, my loss of faith in nutrition as a front-line approach to healing, and various other sundries I’ve been storing up in my brain-attic.
But then COVID-19 happened, and if that isn’t the biggest cosmic plan-changer that ever did plan-change, then I don’t know what is. So we’re gonna roll with it. And at the risk of writing something that’ll already be outdated by the time I hit publish (such is the nature of current events), I’m hoping this post will stay evergreen (or at least ever-chartreuse) by sheer virtue of its universal core theme: navigating conflicting, emotionally charged narratives in which objectivity behooves us but doesn’t come easy.
So LET US BEGIN.
In case you didn’t notice, the cyber-world (and its 3D counterpart, I assume, but we’re not allowed to venture there anymore) is currently a hot mess of Who and what do we believe? This is zero percent surprising. Official agencies have handled COVID-19 with the all grace of a three-legged elephant—waffling between the virus being under control/not under control/OMG millions dead/wait no 60,000/let’s pack the churches on Easter!/naw, lockdown-til-August/face masks do nothing/face masks do something, but healthcare workers need them more/FACE MASKS FOR EVERY FACE RIGHT NOW PLEASE AND THANK YOU/oh no a tiger got the ‘rona!; on and on. It’s dizzying. Maddening. The opposite of confidence-instilling. And as a very predictable result, guerrilla journalism has grown to fill the void left by those who’ve failed to tell us, with any believability, what’s going on.
Exercising our investigative rights is usually a good thing. You guys know me. I’m all about questioning established narratives and digging into the forces that crafted them. It’s literally my life. Good things happen when we flex our thinking muscle, and nothing we’re told should be immune to scrutiny.
But there’s a shadow side here, too—what I’ll henceforth refer to as “lopsided skepticism.” This is what happens when we question established narratives… but not the non-established ones. More specifically, when we go so hog wild ripping apart The Official Story that we somehow have no skepticism left over for all the new stuff we’re replacing it with.
And that, my friends, is exactly what’s happening right now.
I’ve been watching homegrown theories about COVID-19 spiral through various social platforms, born from a mix of data (sometimes) and theory (usually) and anecdote (always). They’re generally a pushback against the mainstream narrative about the coronavirus’s timeline, severity, concern-worthiness, fatality rate, treatment, infection breadth, classification guidelines, origin… round and round we go. Some theories are reasonable (“Has the virus been here longer than we think?”), some are untenable (“The ‘virus’ is actually radiation poisoning from 5G towers!”), and many more lie somewhere between.
Most importantly, they all have one thing in common: a tendency to embrace any and all supportive data without, well, making sure it’s true.
Y’all know what I’m talking about. Evidence we’d never give the time of day if it didn’t work in our favor. The “I remember reading somewhere…”, the “I have a friend who knows someone who…”, YouTube interviews that are impossible to fact-check (but please just trust this person’s top-secret info from an organization they can’t name without the Feds beating down their door), crowdsourced anecdotes, retracted papers, retweeted screenshots of Facebook comments from people whose names and profile pictures are blacked out, the whole shebang.
This stuff. Is. EVERYWHERE.
Unfortunately, throwing a bunch of really bad evidence together can create the illusion of a well-supported theory. And this is what’s happening, my dudes. This is what it’s come to. In our rabid quest to undermine the Powers That Be and figure out what’s really going on, we’ve thrown quality control out the window and become that which we loathe: loyalists to narrative over data.
Case in point, let’s look at what might be the most popular COVID-19 theory circulating right now: that mortality stats are getting padded by assigning deaths to COVID-19 that are really from other causes—thereby making this whole thing seem worse than it actually is. Depending on the sub-theory, this might be due to financial incentives for hospitals (more COVID-19 patients = more $$$); a coordinated government hoax to trick people into relinquishing their sovereignty; a way to butter us up for mass ID microchipping; something something lizard people; and so on.
And from what I’ve seen—and by all means correct me if I’m missing something—this theory draws on the following claims:
This theory would be pretty awful if it’s true. We’d have been got. Duped. Manipulated AF. But how solid is the evidence? Have we actually peeled this thing apart piece by piece before getting all ragey about the injustice of it all?
Oh, we haven’t? Well GUESS WHAT WE’RE GOING TO DO NOW?
Let the unpeeling commence.
1. First, the whole “CDC is telling people to report COVID-19 deaths without testing!” ordeal. The damning bits come from the CDC’s COVID-19 reporting guide (PDF), which gives permission to use COVID-19 on a death certificate if it’s “suspected or likely” and “‘probable’ or ‘presumed’”:
And also says it’s okay to report COVID-19 without testing confirmation:
And the WHO’s “Emergency use ICD codes for COVID-19 disease outbreak” gives a whole death code for COVID-19 cases that aren’t confirmed via test:
And finally, this National Vital Statistics System document says COVID-19 can be put on a death certificate when it’s “assumed” to have caused death:
The point of contention here, which has sparked something of an outrage in important places such as Twitter, is that these guidelines allow a level of guesswork that could mess things up real bad. Especially if there’s already some sort of incentive to bend data in the direction of more coronavirus deaths. What if people assign COVID-19 willy nilly to anyone who has a cough or fever? Or who had a poorly-timed bout of allergies? Where does the line get drawn? For sure, “probable,” “presumed,” “suspected,” and “likely” aren’t very reassuring words when it comes to a disease we’ve shut down the whole globe to contain.
But is this actually conspiracy worthy? And, in a clinical setting, with actual doctors doing doctor things rather than us internet-dwelling oafs imagining how it all might go, would these guidelines really lead to a significant over-reporting of COVID-19 deaths?
For starters, let’s look more closely at that CDC reporting guide. Although it does say COVID-19 deaths can be assigned without a positive test result, it also emphasizes the importance of drawing from all available evidence in order to make an informed judgment:
And it turns out, this is really no sketchier than the CDC’s guidelines for certifying pretty much any cause of death. Seriously. According to the agency’s Medical Examiners’ and Coroners’ Handbook on Death Registration and Fetal Death Reporting (PDF), it’s okay to use personal “judgment” when there’s uncertainty:
And yes, medical examiners and coroners are invited to give their “opinion”:
So are physicians, according to the CDC’s Physician’s Handbook on Medical Certification of Death—note also the use of “probable”:
And medical examiners are broadly allowed to list “causes that are suspected,” and to “use words such as ‘probable’ or ‘presumed’”—again, for any death-cause:
And here we see the CDC’s Instructions for Completing the Cause-of-Death Section of the Death Certificate telling us again that a condition can be listed as “probable” even if there isn’t a definitive diagnosis (and also the words YOUR and OPINION written in CAPS because the CDC successfully learned how to yell on the internet; good job, CDC):
*I know it’s tiny; click for bigger
Are you sick of this yet? Guess what? Alzheimer’s deaths can get the same code whether the disease is confirmed or “probable”:
Oh hey, remember 83 seconds ago when we were so mad that COVID-19 deaths could be listed as “probable” or “presumed”? Because it seemed like some unique-to-coronavirus word twist intended to help pad the death stats? REMEMBER?
No. Just no. This same language is consistent through all the cause of death guidelines, no matter the killer in question. It’s been that way for years. And COVID-19 is even lucky enough to get separate codes for “probable” versus “confirmed” cases, which is more than we can say for some other diseases. (And to boot, some places were already seeing COVID-19 mortality explode before reporting the “probable” deaths at all.) Heck, the guidelines for coronavirus deaths are far more straightforward than the maze-like estimation formula the CDC takes for flu mortality.
In short—and please make me eat my words if I’ve overlooked something important here—this really isn’t outrage-worthy. Certifying any form of death is an imperfect, partly subjective process, and concessions for that reality are baked into all sorts of official guidelines. If overzealous COVIDing is happening (and you’re welcome to investigate any theory-offshoots that it is), it’s not because the CDC told death certifiers to cook the books.
2. As for pneumonia deaths getting classified as COVID-19 deaths? This graph of CDC data has been making the rounds as evidence that something very shady, very shady indeed, is going on. As you can see, around week 10 of this year (starting March 2nd), pneumonia mortality told its wife it loved her and then jumped off a cliff:
If we’re already primed to think the COVID-19 numbers are being doctored, we might take this graph at face value and add it to our stash of outrage fodder. But that would not be smart, friends. Face value is where critical thinking goes to die. And so, in the spirit of questioning literally everything, we must ask: could anything else explain what we’re seeing?
As a matter of fact, yes! So much yes! We only have to venture as far as the CDC’s Provisional Death Counts for Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) page to see what’s up. Go take a look. Especially the “Delays in reporting” section. Thar be some gold.
Basically, the CDC’s death-certificate-processing system is a slow, laborious beast that ensures any recent mortality data is always incomplete. They give a decent rundown of how death certificates get handled from start to finish:
Provisional counts of deaths are underestimated relative to final counts. This is due to the many steps involved in reporting death certificate data. When a death occurs, a certifier (e.g. physician, medical examiner or coroner) will complete the death certificate with the underlying cause of death and any contributing causes of death. In some cases, laboratory tests or autopsy results may be required to determine the cause of death. Completed death certificate are sent to the state vital records office and then to NCHS for cause of death coding.
And here we have a special shoutout to our favorite infectious diseases, noting that pneumonia, flu, and COVID-19 certificates take extra long to trickle into the data pool due to manual coding (emphases mine):
At NCHS, about 80% of deaths are automatically processed and coded within seconds, but 20% of deaths need to manually coded, or coded by a person. Deaths involving certain conditions such as influenza and pneumonia are more likely to require manual codingthan other causes of death. Furthermore, all deaths with COVID-19 are manually coded. Death certificates are typically manually coded within 7 days of receipt, although the coding delay can grow if there is a large increase in the number of deaths. As a result, underestimation of the number of deaths may be greater for certain causes of death than others.
Zooming in even further, the CDC gives some stats conveying just how incomplete their recent data is, and boy howdy is it a sorry sight. At any given moment, data from two weeks ago is likely to be barely over a quarter complete, while data from eight weeks ago is still less than three-quarters complete:
Previous analyses of provisional data completeness from 2015 suggested that mortality data is approximately 27% complete within 2 weeks, 54% complete within 4 weeks, and at least 75% complete within 8 weeks of when the death occurred. Pneumonia deaths are 26% complete within 2 weeks, 52% complete within 4 weeks, and 72% complete within 8 weeks (unpublished). Data timeliness has improved in recent years, and current timeliness is likely higher than published rates.
The CDC even slaps this little disclaimer after each table of COVID-19, pneumonia, and flu death counts:
Once again, with feeling: CDC mortality figures are initially very incomplete, low-balled-as-all-get-out, and retroactively fill in over time. Which means a weird pneumonia death-drop will show up any time we check the most recent data, COVID or No-vid.
To illustrate, Joseph Dunn graphed the CDC’s pneumonia data as it appeared on the same mid-March week of each year since 2013. Behold:
Look at all them swan dives!
And data scientist Tyler Morgan even went to the trouble of graphing the data from every weekly CDC pneumonia report published in the last decade, to show how the lines shift as data gets back-filled. Click here or on the image below for the really cool animation (it’s weirdly beautiful and absolutely worth the 30 seconds of your life):
In other words, there’s nothing anomalous at all about 2020’s pneumonia trends. Nothing. The popular graph up top is a meaningless piece of hooey and it’s sad that it went viral.
Note: there’s an issue here I’m cognizant of, but intentionally not touching on yet, which is that some people believe the CDC (and any other government organization) literally makes up data from thin air, thus rendering all of the above irrelevant. This level of conspiracy is beyond the scope of this post, but I may try to address it at some point later on. Not from a data angle, but from a psychological one.
3. Here we have the wildly popular claim that people are dying with COVID-19, not really from COVID-19. At least, not in the numbers we’re being told. It’s basically a steroided-up version of Claim #1—just with more trickery and plot-thickness and finger-tenting.
The evidence for this one is a lot harder to fact-check, because there are actually no facts to check. Its trueness rests on us believing that doctors and death-certifiers are being marionetted by evil forces and/or just plumb don’t know what they’re doing.
The closest thing we’ve got to “evidence” are citationless social media statements like the above, which we’re expected to trust because LOOK AT ALL THOSE RETWEETS!, a few well-publicized examples of allegedly mis-assigned COVID-19 deaths, and Youtube interviews with people who are pretty sure they know what’s going on. Like this one, featuring Dr. Annie Bukacek, with nearly 750,000 views at the time of writing.
Apparently, she knows her stuff. And the stuff she knows is that the coronavirus figures are being manipulated!
Hmmm…
Hmmmmmm…
Hmmmmmmmmm.
Serious question: how many of us bothered to look Dr. Bukacek up before thrusting her atop a pedestal of trustworthiness? And sharing her video far across the lands? And assuming she’s an impartial commentator on the whole situation (her praiseful introducer was literally her pastor)? Should we really put faith in someone we didn’t even know existed ten seconds ago just because 1) they’re telling us what we want to hear and 2) an internet headline made them sound prestigious?
By the way, to state the obvious, this is me intentionally and very shamelessly cherry-picking to make a point. Not all of her reviews are bad. Nor do the existing ones necessarily prove she isn’t credible. And if we wanted to be truly fair, we could prod deeper and ask whether she might be getting bad-review-bombed due to her vocal pro-life activism or religious affiliation or anti-vaccine stance (she’s definitely got some haterz). There’s a lot of sticky tricky gray-zone business in evaluating reputation, which is why—whenever possible—we should investigate a person’s claims rather than their character.
But the issue here is that with Dr. Bukacek, we can’t “investigate her claims” without installing cameras into every death certifier’s brain and watching what unfolds within their basal ganglias. So we’re left with only her word. And one person’s word is not useful data. Even if it’s the best of persons and the best of words.
Now, to play devil’s advocate with my own arguments here, there’s another popular video—this one featuring Coronavirus Response Coordinator Deborah Birx—that seems more genuinely suspect. I saved this one for last because it might actually have some merit. In it, Dr. Birx talks about the USA’s “very liberal approach to mortality” and outright states that people who die with COVID-19 are counted as COVID-19 deaths:
Transcript: There are other countries that if you had a preexisting condition, and let’s say the virus caused you to go to the ICU and then have a heart or kidney problem, some countries are recording that as a heart issue or a kidney issue and not a COVID-19 death. Right now we’re still recording it and we’ll—I mean the great thing about having forms that come in and a form that has the ability to mark it as COVID-19 infection, the intent is right now that those—if someone dies with COVID-19 we are counting that [as a COVID-19 death].
It’s not surprising this clip went gangbusters! It seems like a deal-clinching A-ha for anyone who suspected COVID-19 was getting slapped onto every death possible.
However, here and always, context matters. After all, this segment was carefully cropped from a much longer coronavirus briefing from April 7th. And if we listen to the full segment—the audience question that came before this clip, and the follow-up question that came after it, and the follow-up answer Dr. Birx gave, and the addendum answer Dr. Anthony Fauci gave—we can better orient ourselves in the conversation that was happening.
Go have a listen. The relevant stuff starts at the 1:39:07 mark:
Could it be that Dr. Birx thought the question-asker was wondering if lack of testing might cause under-reporting, and tried to reassure her by explaining that the current COVID hotspots are flush with tests? And that people with “heart or kidney problems” wouldn’t be reported as dying from those things if they’d ended up in the ICU from coronavirus? (Especially given that COVID-19 itself can cause cardiac injury and kidney damage?)
It sounds to me like the thrust of the asker’s question—which was more along the lines of “Are we sure we’re not over-counting deaths?!”—went over the heads of the task force, and they addressed a different issue than the one she was trying to get at.
But I can’t read minds. And I can’t prove that it’s not all just political doublespeak and of course they understood the question. And I think there’s far too little information in this video alone to assess it from a “scam vs. not-scam” angle. And most importantly, in the absence of actual mortality data that could clue us in to potential over-reporting, I doubt analyzing this thing to smithereens can bring us any closer to the truth.
But, you be the judge. And speaking of mortality data…
4. Lastly and not leastly: the claim that COVID-19 isn’t actually causing excess mortality; we’re just reshuffling death causes to stack up higher for COVID-19 and lower for everything else. Boom, insta-pandemic!
First, a note. This is a Very Important claim. It’s the supreme ruler of all the claims that came before it and perhaps all those incipient ones that will come after. It has executive power and a VIP card for entry into the most highly guarded chambers of our brains. This is because, unlike causes of death, actual body counts can’t be fudged. This is the one true test. If COVID-19 really is taking lives en masse above and beyond what we’d expect from normal death trends, total mortality is where it’ll show up. If it’s not, then our game of death-code musical chairs will be revealed for the con that it is.
Again: Very Important claim. This is the crux of it, my dear readers.
Fortunately, there’s an easy way to test this claim: looking at total mortality trends in areas that COVID-19 has purportedly ravaged, and comparing that to historical mortality in the same location. An absence of anomalous death spikes—taking into account, of course, delays in processing death certificates and the lag time between infection and dying—would suggest we’re over-reporting COVID-19. And if excess mortality does appear, then we either have to concede that COVID-19 isn’t a nothingburger after all, or propose that some other ghastly, unnamed entity is stealing lives very coincidentally at the same time we have a made-up pandemic.
*Keep in mind, too, that our current near-global quarantine should slash deaths from accidents and certain crimes and infectious disease—and thus “normal” mortality rates for right now would likely be lower than for previous years.
So let’s dig into this. The “COVID-19 is overblown” theory asserts that total mortality isn’t doing anything unusual. At least not significantly so. No more than a bad flu year, let’s say. And depending on the source, we may be furnished with graphs that seem to demonstrate this truth to our hungry, data-seeking eyes, such as the following for England and Wales:
There’s one very big problem here. Check the dates.
Almost universally, the “See, it’s nothing!” graphs use data from mid to late March, when COVID-19 was just starting to pick up steam in the areas it’s most recently terrorized. And in March, there really weren’t massive mortality spikes, except perhaps for Italy. Nothing to see here, folks was true. And no one in the infectious disease world was claiming otherwise. In March, the rumblings of upcoming mortality explosions was what people were getting worried about, not the numbers as they then stood. The whole deal with “exponential growth” is that it’s—wait for it—exponential. This is how we went from 0 reported COVID-19 deaths in the USA on February 15th, 65 deaths one month later, and 30,000 deaths yet another month later.
So let’s see what happens when we look, instead, at more recent data from countries with known COVID-19 outbreaks. (This site is a great starting resource for raw mortality data and some visuals.)
First, here’s what’s up with England and Wales now (source):
And another depiction suggesting COVID-19 deaths may be under-reported (data source and image source):
London, OMG (source):
Excess mortality in Spain as a whole, from December 2019 to April 15 of this year (source):
Madrid, in particular, got clobbered:
And Bergamo, Italy, in which March deaths far surpassed anything seen locally within the past decade (source):
Heck, northern Italy as a whole (source):
Switzerland looking pretty wonky for the 65-and-olders (source):
Total mortality in the Netherlands (source):
A big chunk o’ Europe getting excess-mortalitied (source):
New York City, graphed by the New York Times (article here; viewable with free subscription) (NOTE: this data is almost two weeks outdated and the the April deaths are now many magnitudes higher):
We could do this all day, but you get the point.
Here’s the deal, folks. People. Are. Dying. The mortality trends for COVID-19-affected areas look like what happens when you’re trying to draw a straight line and then sneeze. This is not normal. This is not how things “should” look. We can argue all we want about how accurate the COVID-19-specific data is—and indeed, there’s plenty to argue about— but total mortality doesn’t lie. This is real.
By all means, the above peel-apart is far from complete. I’m sure there are more viral videos we could assess, more statistics to double-check, more anomalies to ponder. The point isn’t to reach a final conclusion here—just to demonstrate the process. The level of detail that must go into investigating a theory before we let ourselves fully entertain it. And if that process seems exhausting, excessive, excruciatingly nit-picky, too time consuming—well, it’s the price of admission for calling ourselves “informed.” Anything less and we’re operating on faith. Which is okay, if that’s our goal. But we must call it what it is.
Now maybe you’re thinking, “Okay, the ‘COVID-19 deaths are getting padded’ theory didn’t really hold up. But what about G5 radiation causing virus symptoms? What about mandatory vaccine agendas getting pushed on the world? What about COVID-19 being a bioweapon? What about what about what about?”
To which I say, Yes! Great! What about them indeed! Put on your best-tailored thinking cap and go find out. Marinate in all the data you can find. Watch out for claims that seem sciencey but trace back to a 4chan post. Be mindful of the universal human tendency to filter out things we disagree with and embrace any evidence that we like. Dig in, first and foremost, with the goal of proving yourself wrong. If you can’t, then perhaps there’s something there.
Of course, I realize the type of deep-dive we did in this post isn’t always possible, and not everyone can sit at home all day opening so many browser tabs that their MacBook freezes with a “System Has Run Run Out of Application Memory” error (anyone else? No? Just me?). Sometimes we need shortcuts. So for anyone who really wants to do the work, to prioritize truth-seeking over ideology, to stay oriented in reality, to let go of false narratives, but who doesn’t have infinite time to do so: here are some questions to ask whenever a new or alternative theory presents itself. Especially a theory we find ourselves enamored with. None of these questions can substitute for ruthlessly investigating, but they can help us stay grounded in situations where our minds easily lead us astray.
It’s easy to trick ourselves into thinking we’re being Good Skeptics when we’ve really only lifted one veil of many. There’s nothing “woke” about rejecting the official story while gullibly swallowing its alternatives.
Rather, waking up means waking up to ourselves. It’s recognizing that the battle of good and evil we project onto the world is playing out daily within ourselves. It’s committing to seeing “what is,” instead of stories about “what is.” It’s spreading our skepticism evenly across the info-scape instead of saving it for the things we already distrust.
So here it is, you guys. This is me groveling at the collective feet of the internet, with one thing to say: to anyone—everyone—listening, we need to reflect on how we’re processing the claims we hear. If we’re going to question official narratives, we need to question alternative narratives with the same degree of rigor. There’s no use retiring our sheeplehood from the mainstream only to rejoin the herd on a different pasture.
Source: Denise Minger
 By Brian Shilhavy
By Brian Shilhavy
With the nation currently gripped by the Coronavirus crisis, and with most of the public lauding the fact that the FDA is fast-tracking a new vaccine to supposedly fight the Coronavirus, with testing beginning already on humans with the experimental vaccine while bypassing animal testing, unknown to most of the public, a meeting was held on March 6, 2020 with the Advisory Commission on Childhood Vaccines (ACCV), under the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
These are quarterly meetings held every 3 months, as required by law, but seldom, if ever, publicized or reported on by the corporate “mainstream” media.
Health Impact News might be the only place where these quarterly meetings are reported, and you can review past reports here. We have been accused of publishing “Fake News” when we publish these reports, but all of the information is available to the public and posted on the Federal Government’s websites.
The Big Tech companies that control so much of the Internet’s traffic, work hard to suppress this information. If you visit one of Health Impact News‘ Facebook Pages, for example, you are likely to see this notice inserted to the top of our page:
The March 6th meeting by the Advisory Commission on Childhood Vaccines included a report from the Department of Justice (DOJ) on cases settled for vaccine injuries and deaths as mandated by the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (NVICP).
The NVICP was started as a result of a law passed in 1986 that gave pharmaceutical companies legal immunity from being sued due to injuries and deaths resulting from vaccines.
If you or a family member is injured or dies from vaccines, you must sue the federal government in this special vaccine court. Many cases are litigated for years before a settlement is reached.
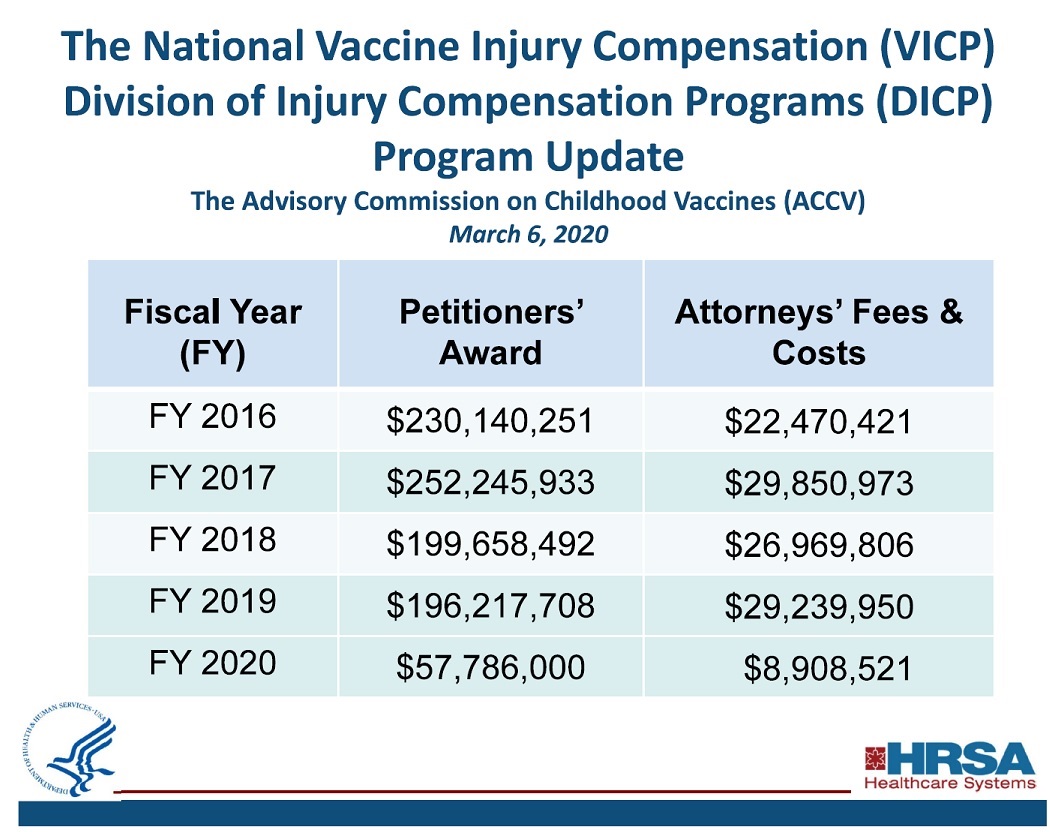
The March, 2020 DOJ report states that 288 petitions were filed during the 3-month time period between 11/16/19 – 2/15/20, with 181 cases being adjudicated and 146 cases compensated.
The March, 2020 DOJ report lists 74 of these settlements for vaccine injuries and deaths, and 60 of those were for damages caused by the flu vaccine. Read more…
5G is the newest wireless networking technology that phones, smartwatches, cars, and other mobile devices, and who knows what else, will use in the coming years, but it won’t be available in every country at the same time.
Some estimates forecast that by 2023, 5G will support more than 10 percent of the world’s mobile connections. For daily updates on how 5G is developing around the globe, see 5G: The Latest News & Updates. Also check out which 5G phones are available right now and when others are coming.
North Americans have already seen smaller iterations of 5G networks pop up, but it’s only just now, in 2020, taking off in most areas due to the elemental challenges of 5G networks. Estimates say that by 2023, up to 32 percent of North American mobile connections will be on a 5G network.
5G fixed wireless broadband internet from Verizon, C Spire, and Starry is currently available at a handful of locations, and Verizon, AT&T, Sprint, and T-Mobile have mobile 5G services available in various cities. More areas will get at-home and mobile 5G this year, from those companies and others like U.S. Cellular.
Rogers Communications began rolling out a 5G network in early 2020 after investing over $4 billion USD on 5G in 2019. They also made a 5G test site on campus at the University of British Columbia. Learn more about the plans Rogers has for 5G to see when they expect a live network around the country.
Canada’s Telus Mobility has given 2020 as the year 5G is available to its customers, but explains that people in the Vancouver area can expect early access.
In late 2017, the Mexican telecommunications company América Móvilannounced the release of 4.5 networks in anticipation of a 5G release.
Its CEO says 5G should be available sometime in 2020 depending on the technology that’s available at that time.
Wireless provider Claro began testing 5G in Puerto Rico in 2019.
Central American countries will most likely see a slow 5G rollout.
Ericsson announced in December 2018, that Tigo had chosen the company to modernize its radio access network. The deal “includes the provision of a 5G-ready multi-standard network.”
There’s no word on when 5G will reach Honduras but this agreement is an important first step.
South American countries with the greatest populations began to see 5G come out in spurts beginning in late 2019.
Entel is the largest telecommunications company in Chile and has partnered with Ericsson to bring 5G wireless service to Chilean customers.
Movistar and Ericsson tested 5G systems in 2017 and will likely roll it out to customers around the same time that Chile sees 5G.
After having signed an agreement to help develop and deploy the technology, we expect Brazil to usher in 5G service starting sometime in 2020.
This time range is also supported by Qualcomm director Helio Oyama, who has stated that 5G will most likely hit Brazil a few years after it’s commercially available elsewhere in 2020.
Telefónica Telecom, Colombia’s largest telecommunications company, will likely have 5G services available for customers in 2020.
In July 2018, Ericsson and Telefónica Telecom demonstrated a 5G data transfer of 27 Gbps in Bogotá.
Telecommunications company Tigo reached a deal with Ericsson to prepare their network for 5G. Ericsson said in December 2018, that they will “expand TIGO’s existing network and modernize the existing 2G/3G and 4G sites, making the network the best fit for TIGO to deliver 5G and IoT services in the future.”
It’s not yet clear when Tigo customers will see 5G in Paraguay, but this deal is definitely a good starting point.
SETAR is Aruba’s leading communications provider, and through a partnership with Nokia, the two expect full coverage on the island by 2022.
5G is live in a handful of areas, with widespread coverage expected this year.
These three South Korean companies collaborated to bring mobile 5G to the country on December 1, 2018: SK Telecom, LG Uplus, and KT. They began with 5G service for select businesses only, but on April 5, opened up 5G for others, too, via the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G.
The SK Telecom service provider started offering 5G service to a wide population on April 5 via their four 5G plans. This came after the company started a limited 5G service with the Myunghwa Industry manufacturing company. SKT’s 5G service plans come after trialing 5G in 2017 and using 5G in their self-driving test site K-City.
LG Uplus’ 5G network went live in Seoul and surrounding locations, with LS Mtron as their first customer. With over 4,000 5G base stations positioned in Incheon, Seoul, and Gyeonggi, the company planned over 7,000 more to be deployed by the end of 2018.
KT Corporation launched pre-commercial 5G services at Lotte World Tower in Seoul and six other areas including Jeju, Ulleungdo, and Dokdo. On April 5, the company launched unlimited 5G services called KT 5G Super Plans, and expanded coverage in Korea to a total of 85 cities by the end of 2019.
KT previously collaborated with Intel to showcase 5G service at the 2018 Olympic Winter Games in PyeongChang, and plans to invest over $20 billionthrough 2023 in 5G and other innovative technologies.
According to the ICT and Broadcasting Technology Policy director at the Ministry of Science and ICT, Heo Won-seok, five percent of the country’s mobile users will be on a 5G network in 2020, and 90 percent by 2026.
NTT DOCOMO is Japan’s largest wireless carrier. They’ve been studying and experimenting with 5G since 2010 and launched pre-commercial 5G services in September 2019 before officially starting 5G services on March 25, 2020.
The 5G service launched with a maximum data rate of 3.4 Gbps that will increase to 4.1 Gbps in June 2020. See the NTT DOCOMO 5G smartphone pagefor device options.
In September 2018, NTT DOCOMO successfully achieved 25–27 Gbps download speeds in a 5G trial with Mitsubishi Electric. The test could be used to develop a high-speed 5G network that works with vehicles.
KDDI and Rakuten are providing 5G services in 2020 as well. KDDI’s 5G network launched on March 26.
SoftBank began its 5G services on March 27 for 1,000 yen /month ($9 USD).
Three wireless carriers launched 5G in China on October 31, 2019: China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom.
However, these companies don’t provide widespread 5G coverage just yet. The most popular areas with 5G in China right now include Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen.
3 Hong Kong launched 5G on April 1, 2020. According to the press release, 5G is expected to cover indoor and outdoor areas in all districts in Hong Kong within 2020.
SmarTone is another company looking into serving 5G in China.
According to Ooredoo, a telecom company in Qatar that has been working on implementing 5G since 2016, they were the first company in the world to provide commercial 5G access.
5G is currently only available in Qatar, but since Ooredoo has markets in Iraq, Oman, Palestine, Maldives, Singapore, Algeria, and other countries, it isn’t a stretch to think that we’ll see 5G reach those areas in 2020.
Ooredoo, in partnership with Ericsson, will also use 5G for home broadband service.
Vodafone is another company providing 5G in Qatar. In late 2018, the company launched a 5G network in Katara Cultural Village and Souq Waqif, and before that, in Abu Hamour, Azizya, Al Mamoura, Al Rayyan, Salwa Road, and Umm Salal Mohammed. Vodafone Qatar offers unlimited 5G plans and a handful of 5G phones.
Two telecommunication companies in Kuwait have launched 5G service.
Zain was the first, announcing the 5G launch in June 2018. You can sign up herefor a 500 GB, 1 TB, 2 TB, or 4 TB plan. Currently, the only device you can use on Zain’s 5G network in Kuwait is the 5G Bolt router, for home broadband internet.
On the same day, just hours later, Ooredoo announced similar news. The 5G plans available from Ooredoo include a 500 GB 45 KWD /month plan and a 1 TB 65 KWD /month plan.
STC (formerly called VIVA) is another telecom company in Kuwait that has launched 5G services. See the 5G coverage map on their website for details.
STC launched a 5G Innovation Center that was created to “explore, develop, and launch new 5G use cases in Kuwait by 2019.” As of February 2019, they had over 1,000 5G NR sites ready to go, and will roll out nationwide 5G services in partnership with Huawei.
UAE 5G became available via Etisalat UAE on May 30, 2019. There are several 5G phones available for purchase.
In early 2019, Etisalat UAE reached a deal with Huawei to “offer its latest state of the art network solutions including 5G wireless, 5G service oriented core and 5G ready transport network to facilitate smooth 5G technology adaption.” Etisalat UAE also selected Ericsson to deploy a 5G network in the United Arab Emirates, both mobile broadband and fixed wireless access.
5G is also coming to the United Arab Emirates from du. Officially called EITC, or Emirates Integrated Telecommunications Company, they announced in early 2019 the rollout of 700 5G sites. Their partners include Nokia and Huawei.
Virgin Mobile is another 5G-ready company deploying this next-gen network across the UAE. See which 5G phones Virgin Mobile has available.
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India released this PDF in late 2017 that outlines the 5G standard draft and shows a timeframe for when 5G should be deployed around the world.
According to Manoj Sinha, the minister of the Department of Telecommunications, India is set to adopt 5G this year: “When the world will roll out 5G in 2020, I believe India will be at par with them.”
On top of that, in August 2018, one of India’s largest telecom providers, Vodafone Idea Limited (previously called Idea Cellular), merged with Vodafone (which was the world’s second-largest phone company before the merger). Vodafone was already preparing for 5G, having set up “future ready technology” in 2017 by upgrading their entire radio network to support 5G.
Reliance Jio is another mobile network operator in India that plans to provide 5G services in 2020, as well as their own 5G handsets.
Another Indian telecom company working on 5G is Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL). They signed a memorandum of understanding with Ciena, a networking systems company, in early 2019 to prepare its network for 5G.
A 5G test network is being erected in 2020 from Cavil Wireless.
Anyone who attended the Asian Games in 2018 could have tried out 5G in Jakarta, Indonesia. A special Telkomsel SIM card was needed in order to connect to the network.
It’s unclear whether Indonesia will see commercial 5G begin to roll out in 2020 or later, but a trial of this size was a great indicator that they’re on a track of some sort. Plus, the company has partnered with Ericsson to upgrade their network in preparation for 5G.
Turkcell is Turkey’s largest mobile phone operator. In early 2017, the company completed a 24.7 Gb/s 5G trial with Ericsson, and in September of 2018 announced an agreement with Nokia to develop 5G technologies.
In November, the company trialed 5G fixed wireless access solutions with Samsung in Istanbul. Turkcell’s CEO commented that “Today, with 5G, we have shown that the latest generation of high-speed wireless access is now possible for our customers. Our goal is clear: to make Turkey one of the first countries in the world with 5G technology.”
In early 2019, the Information and Communication Technologies Authority (BTK) in Turkey approved 5G trials in Istanbul, Izmir, and Ankara. The companies involved include Turkcell, Vodafone Turkey, and TT Mobil.
Turk Telekom is another company looking into bringing 5G to Turkey. In September 2019, the CEO said that the company is the “most ready operator for 5G in terms of fiber infrastructure prevalence.”
It’s clear that Turkcell is on the right path to providing Turkey with 5G, but it’s unclear when, exactly, customers can expect a live network.
Vietnam will see 5G in 2020. According to the country’s state-owned and largest telecom company, Viettel, 5G trials were run in 2019 and they plan to have a network ready in June of 2020.
Mobifone is another mobile network operator that plans to launch 5G in Vietnam by June, 2020.
There are a few mobile network operators in Iran, the largest of which is Mobile Telecommunication Company of Iran (MCI). MCI currently offers “4.5G” internet, which shows that they’re on a path to providing 5G in Iran. They also signed an agreement with Nokia in 2017 to develop 5G technology in Iran.
Iran’s second-largest provider, Irancell, provides both mobile and fixed wireless internet services. In late 2017, in collaboration with Ericsson, the two performed their first 5G test in Tehran and said that 5G will be available in Iran in 2020.
Advanced Info Service (AIS), the country’s largest mobile phone operator, will launch 5G in Thailand in 2020.
Taiwan Star offers its customers a 5G upgrade experience that they can enroll in to take advantage of reduced prices once 5G rolls out in Taiwan.
StarHub announced in November 2018, that they, in partnership with Nokia, completed their first outdoor pilot of 5G on the 3.5 GHz frequency band. However, there’s no information on when StarHub will have a 5G network ready for Singaporean customers.
The IMDA (Info-communications Media Development Authority) is an organization of the Singaporean government that says a 5G network rollout will take place in 2020. There might even be two networks coming to Singapore since IMDA plans to allocate millimeter bands for 5G that “will be sufficient for at least two nationwide 5G networks.”
In fact, all four telcos might bring 5G to Singapore, including Singtel, M1, and TPG Telecom.
The wireless communications company Smart has been testing 5G since 2016 and announced in June of 2018 the launch of 5G TehnoLab, their 5G innovation lab. Smart plans to have a 5G-ready network live for customers in 2020.
In November 2018, Smart rolled out their first 5G cell sites in the Philippines. They were set up in Makati Central Business District (Makati CBD) and at the Clark Freeport Zone in Pampanga.
In Smart’s 5G testing, they’ve managed to achieve speeds of over 14 Gb/s, and have completed a 5G-enabled video call.
Globe Telecom has a 5G fixed wireless broadband service called Globe At Home Air Fiber 5G, offering speeds up to 100 Mbps and data packages as large as 2 TB.
NOW Telecom is another company planning to deploy 5G in the Philippines.
PLDT is hoping to have a 5G network up and running before June 2020.
Although Bangladesh is one of the top 10 most populous countries in the world, it was very slow to roll out 4G and will likely also take much longer than other countries to implement 5G.
In early 2018, the country’s telecom regulator BTRC said that “The world will embrace 5G in 2020. So, we too will have to accept new technology and must move on to 5G. There is no option for procrastination.”
BTRC is expected to auction spectrum for 5G services before the end of 2020 to allow for widespread 5G coverage by 2026.
BTCL and Banglalink are two companies to watch for 5G in Bangladesh.
5G in Malaysia will likely start to be available in specific areas in 2020.
In early 2019, Maxis and Huawei and U Mobile and ZTE signed MoUs (memorandums of understanding) to collaborate on 5G deployment in Malaysia.
TM announced in late 2019 that they’d be participating in the 5G Demonstration Project to test new 5G features and learn how to best deploy 5G in Malaysia. They’ve tested using 5G for smart traffic lights, smart safety and security, and smart parking.
The Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission (MCMC) expects commercial deployment of 5G in Malaysia to take place by the third quarter of 2020.
5G might go live for consumers this year given that the Pakistan Telecommunication Authority prepared for public 5G trials in 2019.
Another tip that 5G is coming to Pakistan is that the country’s 4G pioneer Zongalso became the first company in the country to test 5G services in August 2019.
Telenor Pakistan is looking into bringing 5G to the country as well, but no dates have been released.
5G has been available in Saudi Arabia through Saudi Telecom Company (STC)since June 2019, but only in specific areas of major cities and only through home routers (no mobile option, yet).
According to the company’s CEO:
5G is considered as a very important step toward digitalization and connecting everything, which supports Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 toward economic diversification.
The 5G release in Saudi Arabia took place months after the company reached a deal with Ericsson to launch 5G in the country. STC has also partnered with Nokia to roll out 5G in Saudi Arabia; they announced in early 2019 that the rollout phase had already started.
Another 5G provider in Saudi Arabia is Zain. Over 20 locations have 5G availability, including Riyadh, Al Khobar, Dhahran, Tabuk, Hail, Sabya, Ahad Rafidah, Taif, Bisha, Najran, and Jaizan; see a 5G coverage map here. The Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G and ZTE Axon 10 Pro 5G are Zain’s 5G products.
5G in Bahrain arrived in July 2019 when STC (previously called VIVA) launched their 5G data plans. You can get mobile 5G from STC with one of their 5G phones, or 5G at home with the 5G router. The service is available in areas like Reef Island, Amwaj Islands, and Riffa Views.
Batelco is another company bringing 5G to Bahrain, choosing Ericsson to provide the 5G equipment. Availability is limited to just a few areas as of right now: Amwaj Islands and Reef Island.
5G in Kazakhstan isn’t coming as soon as other countries despite the fact that it’s the ninth-largest country in the world. However, according to Prime Minister Askar Mamin, 5G is definitely in sight, calling for an “Action Plan for the implementation of 5G in Kazakhstan.”
Askar Mamin said in a meeting held in May 2019, that 5G is expected to cover all Kazakhstan settlements that have a population greater than 50 thousand people.
In October 2019, the VEON telecom company launched a 5G trial on a live network.
The country’s second-largest mobile network operator, Mobitel, invested $50 million USD in 2019 to roll out 5G in Sri Lanka.
Mobitel has been working on bringing 5G to Sri Lanka for years. In early 2017, they partnered with Ericsson with the signing of the 5G Island of Innovation Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to bring 5G to Sri Lanka.
Service provider Smart Axiata will most likely be the first company to launch 5G in Cambodia. They were the first service provider to make 4G available in the country in 2014, and followed up in 2019 by showcasing the country’s first 5G live trial. The company expects the first few years of their 5G rollout in Cambodia to be focused on hotspots in major cities.
Viettel Cambodia (MetFone) is another company launching 5G service in Cambodia, in partnership with Telecom Cambodia.
Vodacom Group, which was the first to introduce 4G, 3G, and 2G in South Africa, is at it again with the release of a 5G trial in Lesotho in August 2018. They showcased a fixed wireless access (FWA) network using a temporary license in the 3.5 GHz band.
Vodacom’s 5G network should launch this year through the use of Liquid Telecom, which will provide nationwide 5G wholesale services to the market in early 2020.
Rain is another South African telecom that’s rolling out 5G. From November 11, 2019 and onward, Rain customers can access the 5G network from home in parts of Johannesburg and Tshwane, with more areas becoming available throughout 2020. Check 5G coverage in South Africa with the Rain coverage map.
MTN Group Limited partnered with Ericsson in November 2018, to deploy a fixed wireless access 5G site in Midrand. Although MTN South African hasn’t announced a 5G release date, the trials and tests they’ve performed shows that they’re interested in developing 5G applications and might one day offer customers a 5G network.
Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) plans 5G to roll out in 2020.
Tigo Senegal and Ericsson are working together to upgrade its network to roll out LTE across 1,000 sites. While this isn’t 5G service, it is an important stepping stone.
Although a 5G release date for Egypt isn’t yet known, Telecom Egypt and Nokia agreed in early 2019 to introduce a 5G network.
The telecom company Inwi, which covers over 90 percent of the country with mobile internet access, is bringing 5G to Morocco.
The two other licensed telecom companies in Morocco are Orange Morocco and Maroc Telecom, but both have been silent on a 5G deployment in the country.
The release date for 5G in the Congo is unclear, but according to Léon Juste Ibombo, the country’s minister of Posts, Telecommunications and Digital Economy, we know that the 5G rollout will involve Applus and Congo Telecom:
Investments in Congo’s telecommunications sector are astronomical and the state needs credible companies to help it implement the digital economy ecosystem. This company will help our incumbent operator, Congo Telecom, to implement 5G.
Ooredoo Tunisia has partnered with Nokia through the use of the company’s AirGile cloud-native core, to transition Ooredoo to a place where it can provide Tunisia customers with 5G.
Safaricom will likely launch 5G in Nairobi in early 2020.
5G networks are live right now in some European countries, and others will get 5G during 2020.
Telenor, the country’s biggest telecom operator, launched 5G in Norway in March, 2020, following early testing from 2017. These locations currently have access to the 5G network: Kongsberg, Elverum, Bodø, Askvoll, Fornebu, Kvitfjell, Longyearbyen and Spikersuppa in Oslo, and Trondheim.
Telia Company is another mobile network operator in Norway that opened its first 5G test network in December 2018. Their first trial partner was the Odeon movie theater in Oslo, marking the world’s first 5G cinema. Managing director of Telia Norway said in their December press release, “We are going to develop 5G-based solutions industry by industry, area by area.”
Telia Norway also partnered with Norwegian ISP Get to launch a 5G pilot in a family home, complete with smart tech from Futurehome. Get’s product director said “This family is far ahead of the rest of us, with a home filled with clever things connected through 5G. It is something the rest of us will not experience for several years, but it’s really fun to see what we will get with the latest technology.”
According to the 5G Strategy for Germany, released by Germany’s Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure (BMVI), trial installations began in 2018 with a commercial launch in 2020. 5G is planned to be rolled out “over the period to 2025.”
Deutsche Telekom rolled out 5G in Germany in Berlin, Darmstadt, Munich, Bonn, and Cologne in September 2019. Connectivity is possible through the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G, Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G, Huawei Mate 20 X 5G, and HTC 5G Hub. A total of at least 20 major German cities will have 5G by the end of 2020, and they plan to cover 90 percent of the country with 5G by 2025.
Another German telecom company that has launched 5G services in the country is Vodafone. They turned on their first 25 base stations on July 16, 2019, added Berlin a month later, and made it a goal to have 50 running before the end of August 2019. Customers can use 5G with the Huawei Mate 20 X 5G and Samsung Galaxy S10 5G.
Broadband telecom provider Telefónica Germany revealed in December 2018, that in collaboration with Nokia, they finished building their “Early 5G Innovation Cluster” in Berlin. It will be used to “test and measure the performance and coverage of first 5G services in a dense urban area.”
German ISP United Internet AG is another potential 5G player, having announced in early 2019 that they’d be taking part in a 5G spectrum auction.
Vodafone will provide 5G services to customers in Karlovy Vary by July 2020. This will come a full year after the company tested a 5G holographic call in the same city.
The UK’s largest network operator, EE, was the first to launch 5G in the UK on May 30, 2019. Service started in London, Cardiff, Edinburgh, Belfast, Birmingham, and Manchester, and the company now operates the 5G network in over 70 cities and towns.
EE was also the first in the world to offer the OnePlus 7 Pro 5G smartphone, but they also offer their customers the Samsung Galaxy S20 Ultra 5G, OPPO Reno 5G, LG V50 ThinQ, and other 5G phones. See their list of 5G phones for all of them.
Vodafone UK is another big mobile telecommunications provider in the UK. After testing how 5G can be used in car communications and successfully completing a holographic phone call using 5G, they launched their fifth-gen network in seven cities on July 3, bringing their total 5G coverage to 15 UK locations. The Vodafone 5G phones you can use on the network include the Samsung Galaxy S10 5G and Xiaomi Mi MIX 3 5G.
After announcing their commitment to invest billions in 5G, UK’s Three is another company that launched 5G in the UK, accessible first with Huawei’s 5G phone. After testing 5G for home use, the company also launched their 5G home broadband service on August 19 in London. Three has a list of everywhere you can get their mobile 5G in the UK.
BT Mobile launched 5G services in the UK on October 11, 2019, in 20 cities. See the 5G phones and plans you can get with BT Mobile.
O2 has a 5G network in the United Kingdom, too. It’s currently available in 20 locations, including London, Edinburgh, Cardiff, Belfast, Leeds, Slough, Leicester, Lisburn, Manchester, Birmingham, Glasgow, Liverpool, Newcastle, Bradford, Sheffield, Bristol, and other locations. There are several 5G phonesyou can use on the O2 5G network.
Tesco Mobile uses O2’s network and also began offering 5G to its customers in early 2020.
CityFibre and Arqiva are two more companies with 5G trials in London. They’re in the process of creating a “5G-ready network platform nationwide that will provide the best network at the best economics for Mobile Network Operators.”
Vodafone launched 5G in Italy in these five cities in June 2019: Naples, Bologna, Milan, Turin, and Rome. The company plans to roll out 5G to 100 cities by 2021. There are several 5G phones you can buy through Vodafone’s website.
TIM (Telecom Italia), the largest telecom provider in Italy, made 5G available in Naples, Rome, and Turin as of July 5, 2019. Their 5G network went live in another six cities before the start of 2020: Milan, Bologna, Verona, Florence, Matera, and Bari. By 2021, 120 towns and cities will be covered with TIM’s 5G network.
Iliad, in partnership with Nokia, will deploy 5G across Italy.
The first 5G network in Switzerland went live April 17, 2019, via Swisscom. It launched in 54 towns, including Basel, Bern, Chur, Davos, Geneva, Lausanne, and Zurich. According to Swisscom, more than 90 percent of the population is covered.
Swisscom currently offers the OPPO Reno 5G, LG V50 ThinQ 5G, and Samsung Galaxy S10 5G smartphones, but will have more available from other companies, such as Huawei, later in the year. These devices will work everywhere there’s 5G service from Swisscom, through their inOne mobile subscriptions.
The country’s second-largest telecommunications company, Sunrise, is also working to release 5G in Switzerland. They’ve already covered over 200 cities/villages with 5G, blanketing 80–98% of Dietikon, Bülach, Opfikon, Autafond, and other locations with 5G coverage. There’s a Sunrise 5G coverage map available, which also lists all the areas you can get Sunrise 5G service in Switzerland.
The company currently offers four 5G smartphones: Samsung Galaxy S10 5G, Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G, Huawei Mate 20 X 5G, and Xiaomi Mi MIX 3 5G. They also provide the HTC 5G Hub.
Sunrise ran an ultrafast, 3.28 Gbps 5G test in late 2017, erected their first 5G antenna in mid 2018, and then in November 2018, made live their first standardized 5G network at a ski resort.
Salt (formerly Orange Communications) is another telecom company planning 5G in Switzerland. They revealed in January 2019 that they selected Nokia to upgrade their radio and mobile core network to provide mobile 5G services.
Vodafone Spain was the first operator to launch 5G in Spain. On June 15, 5G became available to customers in these locations:
See if your specific address has 5G coverage with the Vodafone Mobile Coverage Map.
According to Vodafone, 5G speeds at launch can be up to 1 Gbps, but will increase to up to 2 Gbps before the end of the year. You need a 5G phone from Vodafone Spain to access the network.
After initially purchasing spectrum to implement 5G, Vodafone Spain launched 5G trials in various cities in June 2018, including Madrid, Valencia, Seville, and Barcelona. In late 2018, they installed a 5G network node in La Nave, Madrid, and in February 2019 used standards-based 5G phones to complete their first 5G video calls between Madrid and Barcelona.
Orange plans to launch 5G in Spain in 2020. The company revealed in early 2019 that they made their first 5G call using their next-gen network in Valencia and will continue testing the 5G technology in Seville, Vigo, Malaga, Barcelona, Bilbao, and other cities.
Network operator A1 kicked off their path toward 5G in Austria by making their first 5G data connection in Gmünd in early January 2019. See their 5G plans and phones here.
Magenta Telekom (previously called T-Mobile Austria) is deploying 5G mobile base stations across the country following a 110 MHz spectrum purchase in March 2019. In late March, the company revealed several of Austria’s 5G pioneers.
Hutchison Three Austria and ZTE are deploying 5G in Austria, too. Their first business client was in Linz, and with 20 5G sites set up by June 2019, it marked Austria’s first city with continuous 5G coverage.
The Elisa Oyj telecommunications company in Finland opened a commercial 5G network in Tampere in June 2018, claiming to be “first in world to launch commercial 5G.” According to their 5G coverage map, the network is also located in Oulu, Kuopio, Helsinki, Jyväskylä, and other areas.
Elisa has 5G Unlimited plans for 44.90 EUR /month at 1 Gbps and 34.90 EUR /month at 600 Mbps. The ZTE Axon 10 Pro 5G phone can be used on Elisa’s 5G network.
Telia revealed in early December 2018, that Helsinki Airport became the first 5G airport in the world and their first customer using their pre-commercial 5G network. In early 2019, the company began commercial use of its 5G network in three cities and has since expanded to include several more. See the Telia 5G devices you can buy right now for mobile and FWA 5G access.
DNA is another Finnish telecommunications company bringing 5G to Finland. They began offering fixed wireless access service in December, 2019. However, the company says that even with the introduction of 5G, 4G will remain the primary network technology used by most people.
In 2018, Russia’s largest mobile operator, Mobile TeleSystems (MTS), partnered with Samsung to run various 5G tests that included video calls, ultra-low latency video games, and 4K video streaming.
These 5G tests were performed to show that not only is 5G coming to Russia but that Samsung’s 5G routers, tablets, and other devices are fully capable of running on a 5G network.
According to GSMA, 5G networks will cover over 80 percent of the Russian population by 2025, so it can be assumed that a big portion of the country will have access even sooner.
Another indicator that 5G in Russia is coming sooner than later is the 5G research center that’s open in Innopolis, a high-tech city in the Republic of Tatarstan.
Tele2 Russia is another telecom company bringing 5G to Russia. In collaboration with Ericsson, the company announced in February 2019 that they’d deploy 50,000 base stations in Russia. However, Tele2’s CEO says “Before launching 5G networks, Russia must first address several infrastructure issues.”, so customers might have to wait a while to receive 5G services.
Orange is currently the only European telecommunications company that has announced 5G plans for Luxembourg.
It’s unclear when 5G is coming to Slovakia, but mobile operator SWAN Mobilesigned a 5G commercial contract with ZTE in early 2019 to kick off 5G rollout plans. In July 2019, the two performed the the country’s first 5G video call.
In early 2020, Orange Slovensko selected Nokia to prepare its Radio Access Network for 5G.
The telecom giant Vodafone went live with a 5G network in Cork, Dublin, Galway, Limerick, and Waterford on August 13, 2019.
eir’s 5G network is live as well. Its launch locations included Dublin, Limerick, Kilkenny, Waterford, Cork, Galway, Dundalk, and more. There’s an eir 5G coverage map with all the locations.
Vodafone is also working on fixed wireless access. In early December 2018, the company announced that they would begin trials for rural 5G broadband in Roscommon, Gorey, Dungarvan, and Clonmel, covering 20,000 premises.
Imagine is another telecom bringing 5G to Ireland. They announced the launch of their 5G-ready fixed broadband network in February 2019 and plan to build out over 300 sites to cover over one million premises by the fall of 2020.
CEO Sean Bolger had this to say about their 5G plan:
As an Irish company, we are delighted to announce this significant investment and a new approach which will finally solve this problem and deliver much needed, fast and reliable high-speed broadband to homes, businesses and communities across regional and rural Ireland, today and into the future.
Three Ireland is launching a 5G network in the country, too, but it’s not clear when.
Føroya Tele, the Faroe Islands’ largest telecom provider, launched 5G on June 6, 2019.
Jersey Telecom (JT) and ZTE have announced that 5G is coming to the Channel Islands. They began a pre-commercial launch in mid-2019 to test 5G.
5G is being tested in the capital, Minsk, via beCloud.
The Romanian government approved the 5G Strategy in June of 2019.
The 5G Strategy for Romania projects an action plan with concrete tasks and deadlines for deployment, targeting the launch of services in 2020 and 5G service coverage of all urban centers and major land transport routes by 2025.
On June 26 2019, Vodafone Romania launched the country’s first 5G subscriptions. All the details, and the 5G phones you can buy, are available on their Supernet 5G page.
RCS & RDS is the largest Romanian cable and satellite TV company, and they also have 5G available through the Digi Mobil 5G Smart network.
Orange launched 5G in Romania in November 2019. Coverage started in Bucharest, Cluj-Napoca, and Iasi, and will reach more areas throughout 2020. See the Orange 5G coverage map for details.
Magyar Telekom, the largest Hungarian telecom company, launched 5G in Hungary in April 2020. Service began in parts of Budapest and Zalaegerszeg.
Vodafone is another company launching 5G in Hungary. In May of 2019, Vodafone launched Hungary’s first live 5G station in Zalaegerszeg.
Commercial 5G services are expected to come to Croatia by the end of 2020. Service will start in Osijek, within the region of Slavonia.
Telia Company is planning a commercial launch of 5G in Sweden in 2020.
In late December 2018, in collaboration with Ericsson and KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Telia launched a 5G testbed in Stockholm to experiment with 5G applications.
In early 2019, in collaboration with Volvo CE and Ericsson, Telia erected a 5G network in Eskilstuna with the primary focus being industrial use, such as remote-controlled machines.
A Tele2 5G network is coming to Sweden as well. They plan on providing access in 2020, but confirms that it’ll take a few years before the majority of people will have high-speed access.
Polish mobile phone network T-Mobile Polska announced on December 7, 2018, the launch of the country’s first 5G network. It’s currently available only in the center of Warsaw via five base stations, but T-Mobile plans to develop 5G in other locations to reach the entire country.
According to T-Mobile,
Devices providing access to the network have been distributed to selected T‑Mobile partners, so they can be used in order to develop new business solutions and products, which will be eventually offered on the mass market.
Orange is another European mobile network operator that will launch 5G in Poland, but it won’t have a commercially available network up and running until 2020 or 2021.
Polkomtel’s Plus mobile phone network operator is rolling out 5G in Poland in 2020 with Ericsson’s 5G technology. The network will initially be deployed across Warsaw, Gdańsk, Katowice, Łódź, Poznań, Szczecin, and Wrocław.
Vodafone brought Portugal its first 5G connection on December 12, 2018, via a 5G smartphone prototype from Qualcomm. The company also tested a virtual reality game and video call on Ericsson’s 5G network.
ANACOM, Portugal’s communications regulator, will hold a 5G spectrum auction in June 2020 and expects commercial rollouts before 2021.
French regulator Arcep expects commercial 5G rollout in France to take place in 2020.
Orange has launched 5G pilots in France in Lille, Douai, Marseille, and Châtillon.
Iliad, in partnership with Nokia, will deploy 5G across France.
Estonia will likely see a commercially available 5G network in 2020.
The country’s first 5G test network went live on December 20, 2018. It was launched by Telia Company, TalTech University, and Ericsson.
According to Telia Company, the 5G network is a…
testbed for innovation and research for industry partners and academia. TalTech University´s scientists and students, as well as companies and startups can create and test solutions that require fast, high-quality data connection.
One company bringing 5G to Latvia is Tele2. They launched their first 5G base station in Riga in July of 2019, made their first 5G video call a few months later, have released 5G phones, and began offering their 5G network in Daugavpils and Jelgava in early 2020.
Telenor Group brought 5G tests to Denmark in 2019 via Nokia’s AirScale Base Stations.
According to Telenor, the trials:
support 5G use cases such as robotics control, industrial automation, 5G/LTE dual connectivity and Fixed Wireless Access for high performance last mile connectivity.
Telia Company is another mobile network operator that began live 5G tests in Denmark in June 2019.
Mobile telecom company Azercell is planning to launch 5G in Azerbaijan. In early 2019, the company chose Ericsson in a two-year 5G deal to provide the telecom company with radio equipment and related services.
Síminn is the leading provider of wireless communication services in Iceland. They announced in early 2019 that they’d be partnering with Ericsson to deploy 5G-ready equipment to the country.
T-Mobile is promising nationwide 5G coverage in the Netherlands in 2020. In the summer of 2019, T-Mobile announced the launch of three 5G research locations: Scheveningen, The Hague Tech, and the T-Mobile head office in The Hague.
Monaco Telecom customers have access to 5G across all of the Principality of Monaco via the Huawei Mate 20 X and the Xiaomi Mi MIX 3. Full coverage of the entire country was completed in July 2019.
Proximus is the largest mobile telecommunications company in Belgium. Take a look at the Proximus 5G network coverage map for all the details on where you can get 5G in Belgium. You’ll need a 5G mobile subscription as well as a 5G phone that works on the Proximus network, such as the Oppo Find X2 Pro 5G.
In 2019, Orange and Proximus agreed to set up a shared mobile access network, a move that could mean 5G reaches across Belgium even faster.
Vodafone Malta doesn’t have a solid 5G release date yet, but they’re working on bringing 5G to Malta. On October 4, 2019, Vodafone Malta began letting customers try out 5G in areas of Birkirkara, St Julians, and Sliema.
Most major countries in Oceania saw limited 5G roll-out in 2019 with greater availability arriving in 2020.
Australia’s second largest telecommunications company, Optus, launched 5G for mobile and home use on November 4, 2019. The launch involved over 290 5G sites in Sydney, Canberra, Adelaide, Brisbane, Melbourne, Perth, and other locations in NSW, Victoria, and Queensland. See the Optus 5G coverage mapfor details.
Telstra announced in August 2018, that they had enabled 5G technology in areas of the Gold Coast, giving the state of Queensland the country’s first 5G-ready network. They also enabled 5G mobile base stations in Adelaide, Canberra, and Perth in October 2018, and in Melbourne and Sydney in December. According to the CEO, Telstra erected 200+ 5G-capable sites before the end of 2018.
In November 2018, Telstra confirmed that they completed Australia’s very first 5G connection on a live network. The company’s Network Engineering Executive said that they will “continue testing over the coming months to improve data rates and overall performance in readiness for device availability.”
In December 2018, Telstra revealed that their first customer using a 5G device — the HTC 5G Hub — was FKG Group in Toowoomba.
Vodafone has provided a 2020 release date for 5G in Australia. This is a reasonable time frame considering that not only is Vodafone the country’s largest mobile provider but because they partnered with Nokia in 2019 to agree to a 2020 5G rollout. Vodafone users can expect 5G in these areas.
According to Kris Faafoi, New Zealand’s Minister of Broadcasting, Communication and Digital Media,
First allocation of 5G spectrum will be the 3.5 GHz band, with national rights to this portion of the spectrum expected to be auctioned early in 2020.
Having already been laying the groundwork for 5G, and implementing 5G trials in March of 2018, New Zealand’s Spark NZ plans to have a full 5G network ready to go in 2020. They switched on 5G for the first time in September 2019for a limited number of customers, and launched 5G in five other towns in December, 2019.
Vodafone is another 5G player in New Zealand. They switched on 5G in parts of Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, and Queenstown on December 10, 2019. See Vodafone New Zealand’s 5G-ready phones.
5G fixed wireless access arrived in Guam in the second half of 2019 through SK Telecom and IT&E.
According to SK Telecom, the plan has been to start the 5G rollout in Guam in “highly concentrated central areas of cities, local business customers and areas that lack fixed-line infrastructure.” Coverage will then extend to wider areas.
Source: Lifewire
 By Robert F. Kennedy Jr., Chairman, Children’s Health Defense
By Robert F. Kennedy Jr., Chairman, Children’s Health Defense
Vaccines, for Bill Gates, are a strategic philanthropy that feed his many vaccine-related businesses (including Microsoft’s ambition to control a global vaccination ID enterprise) and give him dictatorial control of global health policy.
Gates’ obsession with vaccines seems to be fueled by a conviction to save the world with technology.
Promising his share of $450 million of $1.2 billion to eradicate Polio, Gates took control of India’s National Technical Advisory Group on Immunization (NTAGI) which mandated up to 50 doses (Table 1) of polio vaccines through overlapping immunization programs to children before the age of five. Indian doctors blame the Gates campaign for a devastating non-polio acute flaccid paralysis (NPAFP) epidemic that paralyzed 490,000 children beyond expected rates between 2000 and 2017. In 2017, the Indian government dialed back Gates’ vaccine regimen and asked Gates and his vaccine policies to leave India. NPAFP rates dropped precipitously\
The most frightening [polio] epidemics in Congo, Afghanistan, and the Philippines, are all linked to vaccines.
In 2017, the World Health Organization (WHO) reluctantly admitted that the global explosion in polio is predominantly vaccine strain. The most frightening epidemics in Congo, Afghanistan, and the Philippines, are all linked to vaccines. In fact, by 2018, 70% of global polio cases were vaccine strain.
In 2014, the Gates Foundation funded tests of experimental HPV vaccines, developed by Glaxo Smith Kline (GSK) and Merck, on 23,000 young girls in remote Indian provinces. Approximately 1,200 suffered severe side effects, including autoimmune and fertility disorders. Seven died. Indian government investigations charged that Gates-funded researchers committed pervasive ethical violations: pressuring vulnerable village girls into the trial, bullying parents, forging consent forms, and refusing medical care to the injured girls. The case is now in the country’s Supreme Court.
In 2010, the Gates Foundation funded a phase 3 trial of GSK’s experimental malaria vaccine, killing 151 African infants and causing serious adverse effects including paralysis, seizure, and febrile convulsions to 1,048 of the 5,949 children.
During Gates’ 2002 MenAfriVac campaign in Sub-Saharan Africa, Gates’ operatives forcibly vaccinated thousands of African children against meningitis. Approximately 50 of the 500 children vaccinated developed paralysis. South African newspapers complained, “We are guinea pigs for the drug makers.” Nelson Mandela’s former Senior Economist, Professor Patrick Bond, describes Gates’ philanthropic practices as “ruthless and immoral.”
In 2010, Gates committed $10 billion to the WHO saying, “We must make this the decade of vaccines.” A month later, Gates said in a Ted Talk that new vaccines “could reduce population”. In 2014, Kenya’s Catholic Doctors Association accused the WHO of chemically sterilizing millions of unwilling Kenyan women with a “tetanus” vaccine campaign. Independent labs found a sterility formula in every vaccine tested. After denying the charges, WHO finally admitted it had been developing the sterility vaccines for over a decade. Similar accusations came from Tanzania, Nicaragua, Mexico, and the Philippines.
A 2017 study (Morgenson et. al. 2017) showed that WHO’s popular DTP vaccine is killing more African children than the diseases it prevents. DTP-vaccinated girls suffered 10x the death rate of children who had not yet received the vaccine. WHO has refused to recall the lethal vaccine which it forces upon tens of millions of African children annually.
Global public health advocates around the world accuse Gates of steering WHO’s agenda away from the projects that are proven to curb infectious diseases: clean water, hygiene, nutrition, and economic development. The Gates Foundation only spends about $650 million of its $5 billion dollar budget on these areas. They say he has diverted agency resources to serve his personal philosophy that good health only comes in a syringe.
In addition to using his philanthropy to control WHO, UNICEF, GAVI, and PATH, Gates funds a private pharmaceutical company that manufactures vaccines, and additionally is donating $50 million to 12 pharmaceutical companies to speed up development of a coronavirus vaccine. In his recent media appearances, Gates appears confident that the Covid-19 crisis will now give him the opportunity to force his dictatorial vaccine programs on American children.
Source: Children’s Health Defense
 According to a new breaking news report from Politico, China is once again implementing mass quarantines to combat the coronavirus outbreak after their initial quarantine failed.
According to a new breaking news report from Politico, China is once again implementing mass quarantines to combat the coronavirus outbreak after their initial quarantine failed.
“Henan province in central China has taken the drastic measure of putting a mid-sized county in total lockdown as authorities try to fend off a second coronavirus wave in the midst of a push to revive the economy,” Politico reported. “Curfew-like measures came into effect on Tuesday in Jia county, near the city of Pingdingshan, with the area’s roughly 600,000 residents told to stay home, according to a notice on the country’s official microblog account.”
This breaking news comes at the same time as a new report from Washington Post Beijing bureau chief Anna Fifield stated that the real death toll from the coronavirus in Wuhan, China may be over 40,000, more than 16 times the amount of deaths currently reported by China.
Check out what the The Washington Post reported:
The coronavirus pandemic ravaging the globe officially claimed 2,563 lives in Wuhan, where it began in a market that sold exotic animals for consumption. But evidence emerging from the city as it stirs from its two-month hibernation suggests the real death toll is exponentially higher. …
Using photos posted online, social media sleuths have estimated that Wuhan funeral homes had returned 3,500 urns a day since March 23. That would imply a death toll in Wuhan of about 42,000 — or 16 times the official number. Another widely shared calculation, based on Wuhan’s 84 furnaces running nonstop and each cremation taking an hour, put the death toll at 46,800.
This bombshell report comes not much after Bloomberg News reported that U.S. intelligence officials shared a classified report with President Donald Trump stating that China had lied about how bad the coronavirus was in their country.
“China’s public reporting on cases and deaths is intentionally incomplete,” Bloomberg News reported. “Two of the officials said the report concludes that China’s numbers are fake.”
Vice President Mike Pence also spoke out on the matter: “The reality is that we could have been better off if China had been more forthcoming. What appears evident now is that long before the world learned in December that China was dealing with this, and maybe as much as a month earlier than that, that the outbreak was real in China.”
Dr Deborah Birx, the head of the White House Coronavirus Response also spoke out, indicating that China may have lied about their coronavirus numbers.
“When you talk about could we have known something different, you know, I think all of us, I was overseas when this happened in Africa and I think when you look at the China data originally, and you said, there’s 80 million people, or 20 million people in Wuhan and 80 million people in Hubei, and they come up with the number of 50,000, you start thinking of this more like SARS than you do this kind of global pandemic,” Birx said.
Based on the information that China provided, Birx stated that she did not think that the coronavirus would escalate into a global pandemic.
“So, I think the medical community interpreted the Chinese data as this was serious, but smaller than anyone expected because I think probably we were missing a significant amount of the data” from China, Birx said.
Source: Trending Politics, Politico, Bloomberg & Washington Post