 By Eugene Kiely, Brooks Jackson, Lori Robertson, Robert Farley, D’Angelo Gore, Jessica McDonald, Angelo Fichera and Chelsey Zhu
By Eugene Kiely, Brooks Jackson, Lori Robertson, Robert Farley, D’Angelo Gore, Jessica McDonald, Angelo Fichera and Chelsey Zhu
Summary
We found several false and misleading claims in the October Democratic presidential debate:
- Former Housing and Urban Development Secretary Julián Castro claimed that the most recent jobs data show that “Ohio, Michigan and Pennsylvania … have lost jobs not gained them.” In fact, total nonfarm employment in all three states was up in August — and since President Donald Trump took office — according to the most recent preliminary federal data.
- Former Vice President Joe Biden was wrong when he said that American troops withdrawing from Syria were “being fired on by [Syrian President Bashar] Assad’s people.”
- Activist and former hedge fund manager Tom Steyer claimed 90% of workers haven’t had a raise in 40 years — but a liberal think tank says their real annual wages are up more than 22%.
- Sen. Cory Booker claimed that “raising the minimum to $15 an hour … would put more money in people’s pockets than giving them $1,000 a month” under businessman Andrew Yang’s universal basic income plan. But Yang’s plan would put more money in more pockets than Booker’s bill to raise the minimum wage.
- Leading economists and tax experts disagree about whether Sen. Elizabeth Warren’s proposed wealth tax would generate enough revenue to fund a host of Warren’s education priorities. Yang rightly noted that several European countries repealed their wealth taxes, in part because they did not raise as much revenue as projected. But Warren’s plan seeks to address some of the weaknesses of those plans.
- Yang and Steyer both exaggerated the number of opioid overdose deaths in America by using total drug overdose death figures. Yang also inaccurately attributed all of the deaths to Purdue Pharma.
- Biden claimed Medicare for All will cost “at least $30 trillion over 10 years. That is more on a yearly basis than the entire federal budget.” It may cost that much, but federal spending is projected to exceed $50 trillion over 10 years. And, while Medicare for All would significantly increase federal spending, it also would eliminate health care spending by individuals, businesses and local governments.
- Sen. Bernie Sanders repeated two claims on health care. He said that “500,000 people” are “going bankrupt” due to cancer, but the study he cites only says that medical issues contributed to those bankruptcies — they were not the sole reason. He also said that “87 million Americans are uninsured or underinsured.” The figure includes 19.3 million who were insured but had a gap in coverage in the previous year.
- Sanders referred to climate change as an “existential threat.” Scientists agree climate change does pose a threat to humans and ecosystems, but they do not envision that climate change will obliterate all people from the planet.
- Yang repeated a baseless claim that Amazon is responsible for closing “30% of America’s stores and malls.” In fact, there’s evidence that the number of retail stores may actually be increasing.
Twelve candidates for president met for the Oct. 15 debate hosted by CNN and the New York Times in Westerville, Ohio.
Analysis
Castro Wrong About Job Losses
Castro, a former mayor of San Antonio and HUD secretary, was wrong when he said, “Donald Trump has broken his promises because Ohio, Michigan and Pennsylvania — actually in the latest jobs data — have lost jobs, not gained them.”
In August, which is the most recent month for seasonally adjusted data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, total nonfarm employment went up by 16,500 in Pennsylvania, by 6,100 in Michigan and by 3,700 in Ohio.
Castro’s campaign issued a press release during the debate that said the “data from August … is preliminary due to incomplete data and will be revised by the Bureau of Labor Statistics at the end of this month.” The press release added, “This fiscal year, from March through July, the latest month with final numbers from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, non-farm payrolls are down in Ohio, Michigan, and Pennsylvania.”
That’s all true, but it’s not the claim that Castro made during the debate. The “latest jobs data” for states, although preliminary, is for August — not July.
The estimated job gains in August for Pennsylvania and Michigan surpassed the job losses from March through July. However, Ohio has lost 3,600 jobs from March through August.
Furthermore, the campaign’s argument is misleading. The fact is, since Trump took office in January 2017, total nonfarm employment is up — not down — in those three states and nationwide. That’s whether one measures up to July or August.
Biden Wrong on Syria
Biden mistakenly said that American troops withdrawing from Syria were “being fired on by [Syrian President Bashar] Assad’s people.”
According to news reports, Turkish militias fired artillery rounds near a U.S. military outpost in northeastern Syria last week, though no U.S. forces were injured. There have been no reports of Assad’s Syrian government forces firing on American troops.
Biden: I would not have withdrawn the troops and I would not have withdrawn the additional thousand troops who are in Iraq, which are in retreat now, being fired on by Assad’s people.
After a phone call on Oct. 6 with Turkey’s president, Recep Tayyip Erdogan, President Donald Trump announced he would be withdrawing troops from northern Syria. After initially withdrawing 50 American troops from the Syrian border with Turkey, the Pentagon this week began pulling out all of its 1,000 soldiers from Syria, a process that was expected to take several weeks.
With the U.S. troop withdrawal, Syrian government forces have moved to retake territory in the country’s northeast, but there have been no reports that they have fired upon retreating U.S. forces, as Biden said.
New York Times, Oct. 14: Syrian government forces streamed into the country’s northeast on Monday, seizing towns where they had not stepped foot in years and filling a vacuum opened up by President Trump’s decision to abandon the United States’ Syrian Kurdish allies.
Less than a week after Turkey launched an incursion into northern Syria with Mr. Trump’s assent, President Bashar al-Assad of Syria, considered a war criminal by the United States, has benefited handsomely, striking a deal with the United States’ former allies to take the northern border and rapidly gaining territory without a fight.
News reports made no mention of Syrian forces firing upon withdrawing U.S. troops, though.
Steyer Wrong on Wages
Tom Steyer, the billionaire liberal activist, was wrong when he claimed that “90 percent of Americans have not had a raise for 40 years.”
Even the liberal Economic Policy Institute — a think tank that advocates for low- and middle-income earners — reported in February of this year that the annual wages of the bottom 90% of wage earners have gone up 22.2% since 1979, even after adjustment for inflation. (See Appendix Figure A.)
And that’s only through 2017. Wages have risen further since then. Average weekly earnings of all production and nonsupervisory wage earners in the private sector have gone up 2.1%(after adjustment for inflation) between December 2017 and last month, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
EPI reports that wage growth has been “sluggish” for the vast majority of workers, compared with a 157% increase for the highest-paid 1% of earners since 1979. But Steyer goes too far when he claims there has been no growth at all.
Minimum Wage Hike vs. Universal Basic Income
When asked about how he would convince GM workers to end their strike, Booker took the opportunity to compare his bill to increase the federal minimum wage to $15 an hour to Yang’s universal basic income plan.
Booker: Well, first of all, the one point I wanted to make about the UBI conversation — and I hope that my friend, Andrew Yang, will come out for this — doing more for workers than UBI would actually be just raising the minimum wage to $15 an hour. It would put more money in people’s pockets than giving them $1,000 a month.
Raising the minimum wage to $15 an hour would eventually put more than $1,000 a month in some pockets, but Yang’s so-called “Freedom Dividend” would pay “$1,000 per month, or $12,000 per year, to all U.S. citizens over the age of 18 … no questions asked.”
Booker is a cosponsor of “Raise the Wage Act,” which would increase the minimum wage to $15, but not until six years after enactment. Under the bill, there would be a seven-step phase-in period, beginning with $8.40 an hour and then increasing $1.10 per hour each year for the next six years.
“The annual earnings for a full-time minimum-wage worker is $15,080 at the current federal minimum wage of $7.25,” according to the Center for Poverty Research at the University of California, Davis. An increase to $15 per hour would more than double that to $31,200 — a difference of $16,120, or $1,343 a month.
But it would take five years for a person earning minimum wage to earn more than $1,000 a month in additional income.
Under the Raise the Wage Act, the minimum raise would increase to $8.40 an hour no later than 90 days after the bill is signed into law. That’s an increase of $199 more per month — compared with Yang’s $1,000-per-month plan.
Five years after the bill takes effect, the minimum wage would increase to $13.90 an hour, providing an additional $1,153 per month. The $15 minimum wage would be fully implemented six years after the bill takes effect, providing $1,343 per month in additional income.
After seven years, Yang’s plan would have provided $1,000 a month, while the phasing-in of the minimum wage would provide only an average of $771 a month.
Also, unlike Yang’s plan, the minimum wage pay hike would not affect every American. And increasing the minimum wage to $15 per hour would result in job losses, according to the Congressional Budget Office.
In a July report, CBO said a $15 minimum wage would directly increase the wages of 17 million workers, but “1.3 million other workers would become jobless.”
Yang’s plan would put more money in more pockets than raising the minimum wage.
Warren’s Wealth Tax
As she has in past debates, Warren ticked off a list of things she says could be paid for with her proposal for an annual wealth tax on all assets over $50 million. As we have written, it is a matter of debate among economists and tax experts as to whether her plan would raise as much as she expects.
One of Warren’s challengers at the debate, Yang, noted that several European countries have repealed their wealth taxes “because it had massive implementation problems and did not generate the revenue that they’d projected.” That’s backed up in a report from the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. But the report also argues that a wealth tax is likely needed to close the wealth inequality gap, and it outlines a number of proposed improvements to make a wealth tax more effective than those in Europe. Warren’s plan incorporates many of those suggestions.
Under Warren’s plan, households would pay an annual 2% tax on all assets — net worth — above $50 million, and a 3% tax on every dollar of net worth above $1 billion. During the debate, Warren highlighted some of the things that tax could bankroll.
Warren: And right now in America, the top 0.1 percent have so much wealth — understand this — that if we put a 2 cent tax on their 50 millionth and first dollar, and on every dollar after that, we would have enough money to provide universal child care for every baby in this country, age zero to 5, universal pre-K for every child, raise the wages of every child care worker and preschool teacher in America, provide for universal tuition-free college, put $50 billion into historically black colleges and universities … and cancel student loan debt for 95 percent of the people who have it.
Warren estimates her wealth tax would raise $2.75 trillion over 10 years, based on an analysis by University of California, Berkeley economists Gabriel Zucman and Emmanuel Saez, who study wealth inequality.
When we wrote about Warren’s plan back in June in our story “Facts on Warren’s Wealth Tax Plan,” we noted that several prominent economists and tax experts cast doubt on Warren’s estimate of the revenue the tax would generate, warning that wealthy people would find ways to avoid the tax.
Yang noted that that was one of the reasons several European countries scrapped their wealth tax plans.
Yang: And a wealth tax makes a lot of sense in principle. The problem is that it’s been tried in Germany, France, Denmark, Sweden, and all those countries ended up repealing it, because it had massive implementation problems and did not generate the revenue that they’d projected. If we can’t learn from the failed experiences of other countries, what can we learn from? We should not be looking to other countries’ mistakes.
Indeed, while as many as a dozen countries in Europe had a wealth tax in the early 1990s, that number has dropped to three as of 2018, according to an OECD report. (In 2018, Francereplaced its net wealth tax with a new real estate wealth tax.)
“Decisions to repeal net wealth taxes have often been justified by efficiency and administrative concerns and by the observation that net wealth taxes have frequently failed to meet their redistributive goals,” the report stated. “The revenues collected from net wealth taxes have also, with a few exceptions, been very low.”
However, the report “also argues that capital income taxes alone will most likely not be enough to address wealth inequality and suggests the need to complement capital income taxes with a form of wealth taxation.”
The report makes several recommendations to bolster the effectiveness of a wealth tax — lessons learned from the European examples. Warren’s plan has attempted to incorporate many of those suggestions.
For example, the OECD report recommends a wealth tax only be levied on the very wealthy, that the rate should be low, exemptions and reliefs should be limited (to prevent those subject to the tax from moving assets into exempted categories), and that payments should be allowed in installments for those “facing liquidity constraints.” All of those are part of Warren’s plan.
Under the Warren plan, those with liquidity issues would be able to defer tax payments, with interest, for up to five years. And to guard against wealthy Americans simply moving out of the country to avoid the wealth tax, Warren’s plan would assess a one-time 40% “exit tax” on the net worth above $50 million for those who renounce their citizenship.
We take no position on whether those provisions in the Warren plan would address the lower-than-expected revenues generated by some European countries that tried a wealth tax, but we simply note that there is significant disagreement among economists and tax experts.
Biden on Medicare for All
As he has done in past debates, Biden repeatedly criticized the Medicare for All proposal as a budget buster, saying it would increase federal spending by $30 trillion over 10 years. But Biden ignored that nearly all health care spending by businesses, local governments and individuals would go away.
At one point, Biden said: “The plan is going to cost at least $30 trillion over 10 years. That is more on a yearly basis than the entire federal budget.” He turned to the issue later in the debate, saying something similar: “It costs $30 trillion. Guess what? That’s over $3 trillion — it’s more than the entire federal budget.”
We should start out by saying that $30 trillion over 10 years is not “more than the entire federal budget.” In its August report on long-term budget projections, the Congressional Budget Office estimates federal outlays will be $57.8 trillion over 10 years, from 2020 to 2029.
Also, as we’ve explained before, we don’t know how much Medicare for All would cost, since many details are yet to be determined. But two estimates, one by the Urban Institute and another by the Mercatus Center at George Mason University, said the federal government cost would be $32 trillion or $32.6 trillion over 10 years.
The government would have to raise taxes or fees, or cut other spending, to cover the costs. But Biden ignores the fact that current health care spending by private insurers, employers, individuals and states would shift to the federal government.
Opioid Epidemic
In relating the severity of the opioid epidemic, Yang and Steyer gave inaccurate figures for the number of overdose deaths from opioids.
“I think this is one of the most heartbreaking experiences that America’s had — 72,000 people died of opioid overdoses last year,” Steyer said in response to a moderator’s question about how he would address the opioid epidemic.
Steyer’s statistic, however, is for 2017, and applies to deaths from overdoses from any drug, not just those from opioids. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s website, there were 70,237 deaths from any drug in 2017, with 47,600, or 67.8%, involving opioids.
For 2018, provisional CDC data suggest that overdose deaths fell, to 68,618 deaths from any drug. The agency estimates that 47,625 deaths, or 69%, were opioid-related.
The 72,000 number that Steyer used is well known because it was widely reported as a provisional 2017 figure from the CDC in August 2018 (the final data, which we report above, differs slightly, and is limited to U.S. residents).
Yang made a similar error when he claimed that Purdue Pharma was responsible for eight deaths per hour.
Yang: There was a point when there were more opiate prescriptions in the state of Ohio than human beings in the state of Ohio. And for some reason, the federal government thought that was appropriate. They ended up levying a $600 million fine against Purdue Pharma, which sounds like a lot of money, until you realize that company made $30 billion. They got a 2% fine, and they killed tens of thousands of Americans, eight an hour.
We contacted the Yang campaign to find out the source of the eight deaths an hour claim, and we were directed to a Vox news article reporting on the initial 2017 estimate of 72,000 overdose deaths, which noted that the death toll was equivalent to nearly 200 per day. The campaign then spelled out the math, explaining that 200 divided by 24 hours was 8.33.
The math checks out, but as with Steyer, those eight deaths per hour were not due just to opioids. Rather, opioids were involved in about 5 deaths per hour in 2017.
Yang’s other error is to ascribe all of the overdose deaths to Purdue Pharma. While Purdue Pharma, as the maker of OxyContin, is arguably responsible for many opioid-related deaths, the company isn’t responsible for all of them.
Medical Bankruptcies and the ‘Underinsured’
Sanders stated that “500,000 people” are “going bankrupt” because “they came down with cancer.” As we wrote in September, Sanders is referencing a March 2019 editorial article in the American Journal of Public Health. Of the 910 respondents who declared bankruptcy between 2013 and 2016, 66.5% said medical expenses or medical problems either “somewhat” or “very much” contributed to their bankruptcies. This percentage translates to just under half a million bankruptcies when applied to the 750,489 non-business bankruptcies filed from 2015-2019.
Medical issues weren’t the sole reason for some of those bankruptcies. Also, the survey did not ask about specific medical conditions, so there’s no evidence those bankruptcies happened only because of medical expenses related to cancer or any other disease.
Sanders repeated another claim he has made in previous debates, saying that “87 million Americans are uninsured or underinsured.” As we’ve written before, this figure comes from a Commonwealth Fund study and includes 19.3 million who were insured when they were surveyed but had a gap in coverage in the previous year.
“Of the 194 million U.S. adults ages 19 to 64 in 2018, an estimated 87 million, or 45 percent, were inadequately insured,” the study said. It broke down the “inadequately insured” into three different categories: 24 million uninsured, 43.8 million who were “underinsured” and 19.3 million who were insured but had been uninsured at some point in the prior year.
Climate Change
Debate moderators did not ask candidates about climate change, but that didn’t stop a few candidates from referring to it, including Sanders, who used a descriptor that could use some clarification.
“We’re forgetting about the existential threat of climate change,” Sanders said early on in the debate.
“Existential” has become a popular word among Democrats to describe the danger that climate change poses. As we’ve written in our coverage of a previous debate, it’s not entirely clear what politicians mean when they use the word. But if taken literally to mean the end of humanity, the descriptor is incorrect.
Penn State climate scientist Michael Mann told us previously in an email that the idea that humans would go extinct because of climate change “simply cannot be defended scientifically.”
Yet scientists are clear that climate change does pose serious risks to civilization through increased temperatures, sea level rise and extreme weather, among other factors — especially if greenhouse gas emissions continue unabated.
In some cases, this could even mean a specific location would be uninhabitable, said Benjamin Cook, a climate scientist at NASA. But does he think climate change is going to wipe humanity off the face of the Earth? “No,” he said.
Yang Wrong About Amazon — Again
Yang doubled down on a false claim about Amazon.com.
Yang: Amazon alone is closing 30% of America’s stores and malls, soaking up $20 billion in business while paying zero in taxes.
As we reported Aug. 1, after he made the same claim in the second Democratic debate, Yang went way beyond the facts. We found no factual basis for the claim that 30% of stores have closed, and some evidence that the number may be increasing. The National Retail Federation reports that “54 percent of surveyed retailers plan to open new stores in 2019, and 36 percent of those surveyed will have a higher store count than in 2018.” Furthermore, the retail services firm JLL reported last year that 850 new stores were being planned over the next five years by firms that previously had sold only through the internet.
We also noted that the Wall Street Journal has estimated that Amazon paid 8% of its income in taxes for the years 2012 through 2018 — which the Journal noted was “low, but not zero or negative.”
It’s true that a 2017 Business Insider report estimated that 30% of retail malls (not stores) were being pushed “to the brink of death” (but not necessarily over it) by a wave of store closings by old-line retailers including JCPenney and Sears. But malls are not stores, and even that report didn’t cite Amazon’s competition as the sole cause of the malls’ distress.
Sources
Kiely, Eugene et. al. “FactChecking July’s Round Two Debate.” FactCheck.org. 1 Aug 2019.
Cook, Benjamin. Climate scientist, NASA. Interview with FactCheck.org. 26 Jul 2019.
Mann, Michael. Distinguished Professor of Atmospheric Science, Pennsylvania State University. Email sent to FactCheck.org. 23 Jul 2019.
Kiely, Eugene et. al. “FactChecking the Second Democratic Debate.” FactCheck.org. 31 Jul 2019.
Collins, Sara R. et. al. “Health Insurance Coverage Eight Years After the ACA.” The Commonwealth Fund. 7 Feb 2019.
Robertson, Lori et. al. “FactChecking the September Democratic Debate.” FactCheck.org. 13 Sep 2019.
Himmelstein, David U. et. al. “Medical Bankruptcy: Still Common Despite the Affordable Care Act.” Am J Public Health. 109(3):431-433, 2019.
United States Courts. Bankruptcy Filings Continue to Decline. 22 Apr 2019.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. “Employment, Hours, and Earnings from the Current Employment Statistics survey (National); Total Nonfarm Employment, Seasonally Adjusted.” Data accessed 15 Oct 2019.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. “State and Area Employment, Hours, and Earnings (Pennsylvania); Total Nonfarm Employment, Seasonally Adjusted.” Data accessed 15 Oct 2019.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. “State and Area Employment, Hours, and Earnings (Ohio); Total Nonfarm Employment, Seasonally Adjusted.” Data accessed 15 Oct 2019.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. “State and Area Employment, Hours, and Earnings (Michigan); Total Nonfarm Employment, Seasonally Adjusted.” Data accessed 15 Oct 2019.
Castro, Julian. “FACT: Ohio, Michigan and Pennsylvania Have Lost Jobs Under Trump.” Press release. 15 Oct 2019.
Gould, Elise. “State of Working America Wages 2018.” Economic Policy Institute. 20 Feb 2019.
Bureau of Labor Statistics. “Employment, Hours, and Earnings from the Current Employment Statistics survey (National); Average Weekly Earnings of production and nonsupervisory employees, 1982-1984 Dollars.” Data extracted 16 Oct 2019.
Rubin, Richard. “Does Amazon Really Pay No Taxes? Here’s the Complicated Answer.” Wall Street Journal. 14 Jun 2019.
Peterson, Haley and Skye Gould. “Store closures will push 30% of US malls to the brink of death.” Business Insider. 7 Mar 2017.
Aronholt, Bethany. “Setting the record straight on the state of retail and store closures.” National Retail Federation. 15 Apr 2019.
Maloney, Greg. “Once-Online-Only Brands Will Open 850 Brick-And-Mortar Stores Over Next Five Years.” Forbes. 12 Nov 2018.
Congressional Budget Office. “An Update to the Budget and Economic Outlook: 2019 to 2029.” 21 Aug 2019.
Robertson, Lori. “The Facts on Medicare for All.” FactCheck.org. 24 Apr 2019.
Holahan, John, et. al. “The Sanders Single-Payer Health Care Plan.” Urban Institute. May 2016.
Blahous, Charles. “The Costs of a National Single-Payer Healthcare System.” Mercatus Center, George Mason University. Jul 2018.
“What is the Freedom Dividend?” Friends of Andrew Yang. Undated. Accessed 16 Oct 2019.
U.S. Senate. “S. 150, Raise the Wage Act.” (as introduced 16 Jan 2019.)
“What are the annual earnings for a full-time minimum wage worker?” Center for Poverty Research at the University of California, Davis. 12 Jan 2018.
Congressional Budget Office. “The Effects on Employment and Family Income of Increasing the Federal Minimum Wage.” Jul 2019.
LaMothe, Dan. “U.S. forces say Turkey was deliberately ‘bracketing’ American troops with artillery fire in Syria.” Washington Post. 12 Oct 2019.
White House website. “Statement from the Press Secretary.” 06 Oct 2019.
Vanden Brook, Tom. “Pentagon to withdraw 1,000 troops from Syria within weeks, pulling back in fight against ISIS.” USA Today. 14 Oct 2019.
Hubbard, Ben and Schmitt, Eric. “Assad Forces Surge Forward in Syria as U.S. Pulls Back.” New York Times. 14 Oct 2019.
OECD Tax Policy Studies. “The Role and Design of Net Wealth Taxes in the OECD.” 2018.
Farley, Robert. “Facts on Warren’s Wealth Tax Plan.” FactCheck.org. 25 Jun 2019.
OECD iLibrary. “Overview of individual net wealth taxes in OECD countries.” 2018.
Summers, Lawrence H. and Sarin, Natasha. “Opinions: A ‘wealth tax’ presents a revenue estimation puzzle.” Washington Post. 4 Apr 2019.
Saez, Emmanuel and Zucman, Gabriel. “Response to Summers and Sarin, ‘A wealth tax presents a revenue estimation puzzle,’ Washington Post, April 4.” 25 Jun 2019.
CDC. “Drug Overdose Deaths.” Accessed 16 Oct 2019.
CDC, National Center for Health Statistics. “Vital Statistics Rapid Release: Provisional Drug Overdose Death Counts.” Accessed 16 Oct 2019.
Hedegaard, Holly et. al. “Drug overdose deaths in the United States, 1999–2017.” NCHS Data Brief, no 329. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2018.
Ingraham, Christopher. “Fentanyl use drove drug overdose deaths to a record high in 2017, CDC estimates.” Washington Post. 15 Aug 2018.
Sanger-Katz, Margot. “Bleak New Estimates in Drug Epidemic: A Record 72,000 Overdose Deaths in 2017.” New York Times. 15 Aug 2018.
Lopez, German. “2017 was the worst year ever for drug overdose deaths in America.” Vox. 16 Aug 2018.
Allyn, Bobby. “Purdue Pharma, Accused Of Fueling Opioid Crisis, Files For Chapter 11.” NPR. 16 Sep 2019.
Source: FactCheck.org
 According to a new breaking news report from Politico, China is once again implementing mass quarantines to combat the coronavirus outbreak after their initial quarantine failed.
According to a new breaking news report from Politico, China is once again implementing mass quarantines to combat the coronavirus outbreak after their initial quarantine failed.
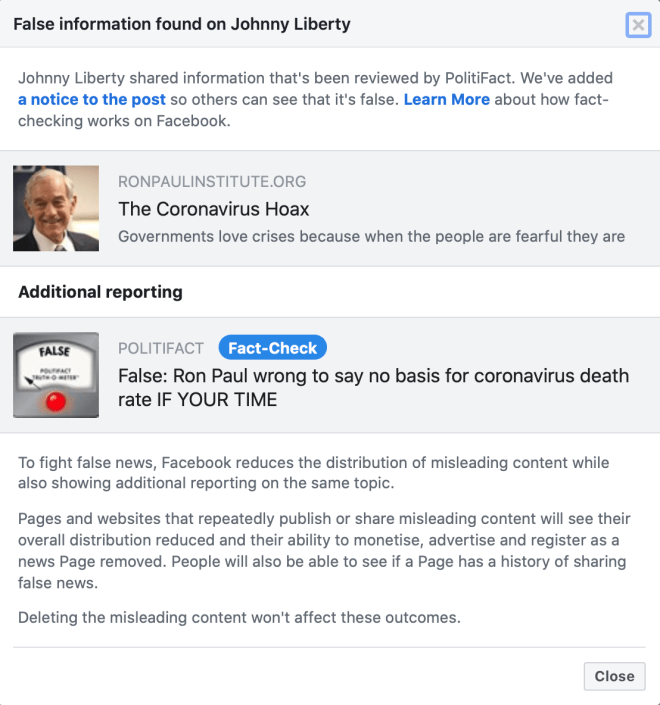 Social media behemoth Facebook has just acted to censor and suppress Ron Paul’s latest weekly column, “
Social media behemoth Facebook has just acted to censor and suppress Ron Paul’s latest weekly column, “
 Jim Jordan, Editor’s Note: So why are not these deaths labeled: heart disease, respiratory disease, diabetes, etc? How these deaths are labeled drives the narrative. Yes, if you have underlying serious health conditions this virus could push that person over the edge; however, that does not mean the COVID -19 is THE CAUSE of death in any of these cases. It is a factor that has to be addressed and perhaps if government and health agencies put this in perspective there wouldn’t be this panic and crashing down of the economies, unnecessary fear and its consequences. Addressing chronic health conditions with better policies would mitigate the consequences of these viral outbreaks.
Jim Jordan, Editor’s Note: So why are not these deaths labeled: heart disease, respiratory disease, diabetes, etc? How these deaths are labeled drives the narrative. Yes, if you have underlying serious health conditions this virus could push that person over the edge; however, that does not mean the COVID -19 is THE CAUSE of death in any of these cases. It is a factor that has to be addressed and perhaps if government and health agencies put this in perspective there wouldn’t be this panic and crashing down of the economies, unnecessary fear and its consequences. Addressing chronic health conditions with better policies would mitigate the consequences of these viral outbreaks. 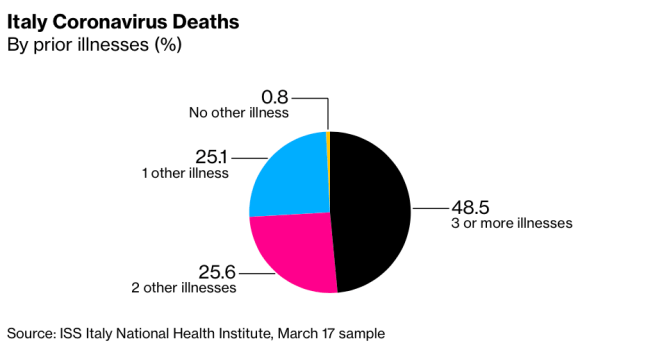 The new study could provide insight into why Italy’s death rate, at about 8% of total infected people, is higher than in other countries.
The new study could provide insight into why Italy’s death rate, at about 8% of total infected people, is higher than in other countries.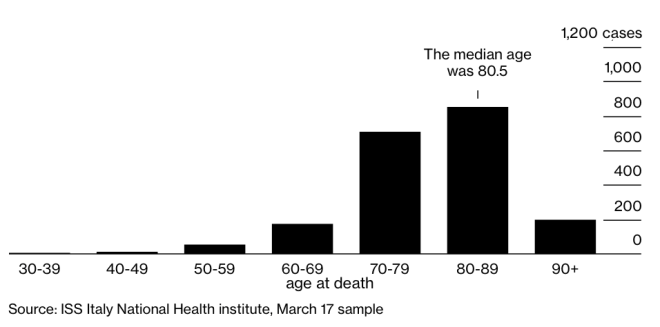 The average age of those who’ve died from the virus in Italy is 79.5. As of March 17, 17 people under 50 had died from the disease. All of Italy’s victims under 40 have been males with serious existing medical conditions.
The average age of those who’ve died from the virus in Italy is 79.5. As of March 17, 17 people under 50 had died from the disease. All of Italy’s victims under 40 have been males with serious existing medical conditions.


